PERADIGM: Phenotype Embedding Similarity-based Rare Disease Gene Mapping
PERADIGM: Phenotype Embedding Similarity-based Rare Disease Gene Mapping
Zheng, W.; Xie, Y.; Gu, J.; Li, H.; Somlo, S.; Besse, W.; Zhao, H.
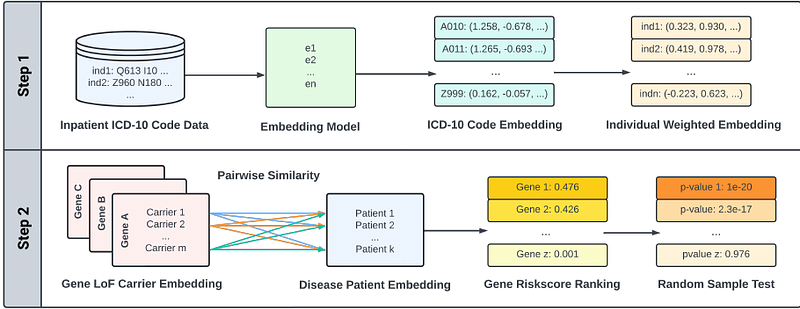
AbstractIdentifying genes associated with rare diseases remains challenging due to the scarcity of patients and the limited statistical power of traditional association methods. Here, we introduce PERADIGM (Phenotype Embedding Similarity-based Rare Disease Gene Mapping), a novel framework that leverages natural language processing techniques to integrate comprehensive phenotype information from electronic health records for rare disease gene discovery. PERADIGM employs an embedding model to capture relationships between ICD-10 codes, providing a nuanced representation of individual phenotypes. By utilizing patient similarity scores, it enhances the identification of candidate genes associated with disease-specific phenotypes, surpassing conventional methods that rely on binary disease status. We applied PERADIGM to the UK Biobank dataset for three rare diseases: autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), Marfan syndrome, and neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1). PERADIGM identified additional candidate genes associated with ADPKD-related and Marfan syndrome-related phenotypes, some of which are supported by existing literature, and demonstrated enhanced signal detection for NF1-specific phenotypes beyond traditional methods. Our findings demonstrate the potential of PERADIGM to identify genes associated with rare diseases and related phenotypes by incorporating phenotype embeddings and patient similarity, providing a powerful tool for precision medicine and a deeper understanding of rare disease genetics and clinical manifestations.