Spatiotemporal dynamics of CD73 in mouse retina under physiological conditions
Spatiotemporal dynamics of CD73 in mouse retina under physiological conditions
Ishii, R.; Sakurai, K.; Hosomi, N.; Fleischmann, B.; Mizuno, S.; Kimura, K.; Yanagisawa, H.
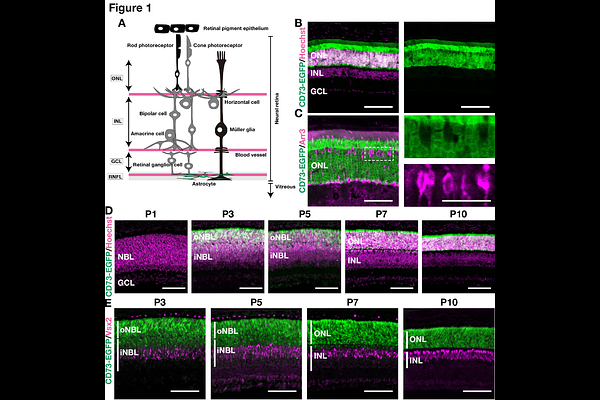
AbstractAdenosine is essential to energy metabolism and neuromodulation in the central nervous system. The retina is a highly energy-demanding neural tissue, and dysregulation of adenosine signaling causes retinal diseases. However, the dynamics of ecto-5\'-nucleotidase (CD73), a key enzyme for extracellular adenosine generation, remain elusive. Here, we investigate its spatiotemporal profile from development to adulthood using two transgenic mouse lines. We found that CD73 is transiently expressed in the early astrocyte lineage (Embryonic day 16.5 to Postnatal day [P] 3), becomes prominent in the rod-photoreceptor lineage by P3, and appears in the inner nuclear layer from P7 onward. CD73 deletion delays rod-response recovery and shortens the implicit time in scotopic ERG under dim light. These findings indicate that light and other physiological cues influence CD73 expression, which has significant consequences for retinal function, thereby providing a foundation for exploring disease-related alterations in CD73 and designing therapies that restore adenosine homeostasis.