TURBO: Automated Total-body PET Image Processing and Kinetic Modeling Toolbox
TURBO: Automated Total-body PET Image Processing and Kinetic Modeling Toolbox
Tuisku, J.; Palonen, S.; Kärpijoki, H.; Latva-Rasku, A.; Tuomola, N.; Harju, H.; Nesterov, S.; Oikonen, V.; Iida, H.; Teuho, J.; Han, C.; Karjalainen, T.; Kirjavainen, A. K.; Rajander, J.; Klen, R.; Nuutila, P.; Nummenmaa, L.; Knuuti, J.
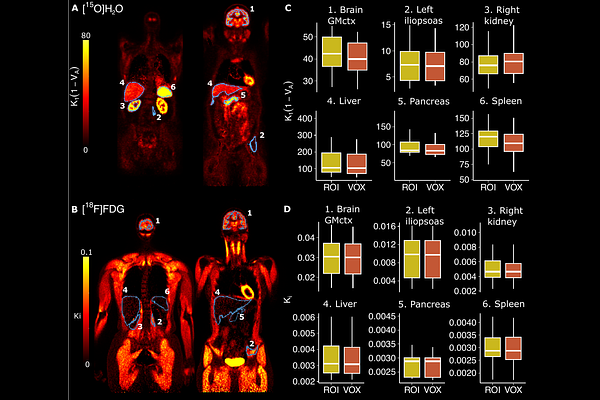
AbstractABSTRACT Total-body PET imaging is a novel concept that requires a high level of automatization and standardization, as the large number of target tissues increases manual workload significantly. We introduce an automated analysis pipeline (TURBO) for preprocessing and kinetic modeling of total-body [15O]H2O and [18F]FDG PET data, enabling efficient and reproducible analysis of tissue perfusion and metabolism at regional and voxel level. The approach employs automated CT segmentation for ROI delineation, image-derived input determination, and region-specific PET data kinetic modelling. Methods: We validated the analysis pipeline using Biograph Vision Quadra (Siemens Healthineers) total-body PET/CT scans from 21 subjects scanned with [15O]H2O and 16 subjects scanned with [18F]FDG using six ROIs (cortical brain gray matter, left iliopsoas, right kidney, pancreas, spleen and liver) representing different levels of blood flow and glucose metabolism. Results: Model fits showed good quality with consistent parameter estimates at both regional and voxel levels (R^2 > 0.91 for [15O]H2O, R^2 > 0.99 for [18F]FDG). Estimates from manual and automated input functions were correlated (R^2 > 0.86 for [15O]H2O, and R^2 > 0.88 for [18F]FDG) with minimal bias (<10% for [15O]H2O and <2% for [18F]FDG). Manually and automatically (CT-based) extracted ROI level data showed strong agreement (R^2 > 0.82 for [15O]H2O and R^2 > 0.83 for [18F]FDG), while motion correction had little impact on parameter estimates (R^2 > 0.83 for [15O]H2O and R^2 > 0.88 for [18F]FDG) compared with uncorrected data. Conclusion: Our automated analysis pipeline provides reliable and reproducible parameter estimates across different regions, with average processing time of <180 min per subject. This pipeline completely automatizes total-body PET analysis, reducing manual effort and enabling reproducible studies of inter-organ blood flow and metabolism, including brain-body interactions.