Bacterial surface lipoproteins mediate epithelial microinvasion by Streptococcus pneumoniae
Bacterial surface lipoproteins mediate epithelial microinvasion by Streptococcus pneumoniae
Chan, J. M.; Ramos-Sevillano, E.; Betts, M.; Wilson, H. U.; Weight, C. M.; Houhou-Ousalah, A.; Pollara, G.; Brown, J. S.; Heyderman, R. S.
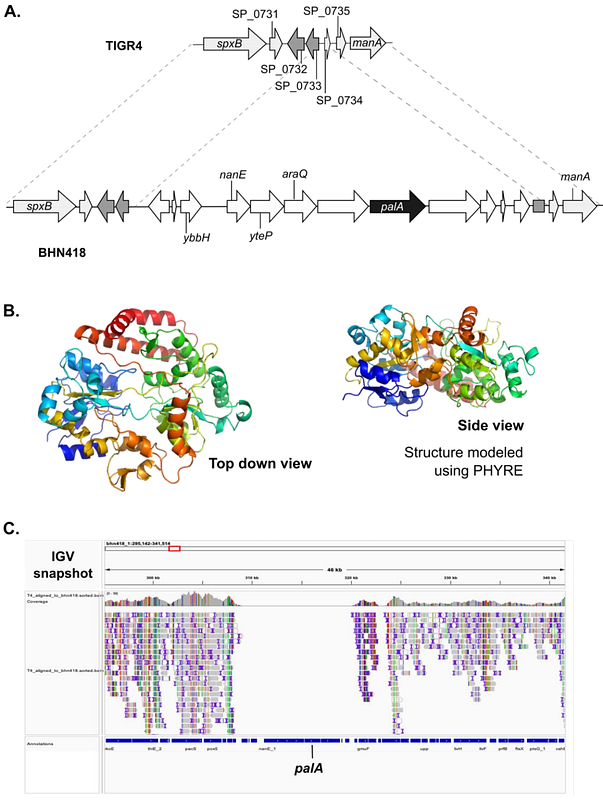
AbstractStreptococcus pneumoniae, a common coloniser of the upper respiratory tract, invades nasopharyngeal epithelial cells without causing disease in healthy people. We hypothesised that surface expression of pneumococcal lipoproteins, recognised by the innate immune receptor TLR2, mediate epithelial microinvasion. Mutation of lgt in serotype 4 (TIGR4) and serotype 6B (BHN418) pneumococcal strains abolishes the ability of the mutants to activate TLR2 signalling. Loss of lgt also led to concomitant decrease in interferon signalling triggered by the bacterium. However, only BHN418 lgt::cm but not TIGR4 lgt::cm was significantly attenuated in epithelial adherence and microinvasion compared to their respective wild-type strains. To test the hypothesis that differential lipoprotein repertoires in TIGR4 and BHN418 lead to the intraspecies variation in epithelial microinvasion, we employed a motif-based genome analysis and identified an additional 525 a.a. lipoprotein (pneumococcal accessory lipoprotein A; palA) encoded by BHN418 that is absent in TIGR4. The gene encoding palA sits within a putative genetic island present in ~10% of global pneumococcal isolates. While palA was enriched in carriage and otitis media pneumococcal strains, neither mutation nor overexpression of the gene encoding this lipoprotein significantly changed microinvasion patterns. In conclusion, mutation of lgt attenuates epithelial inflammatory responses during pneumococcal-epithelial interactions, with intraspecies variation in the effect on microinvasion. Differential lipoprotein repertoires encoded by the different strains do not explain these differences in microinvasion. Rather, we postulate that post-translational modifications of lipoproteins may account for the differences in microinvasion.