Shadows and Observational Images of a Schwarzschild-like Black Hole Surrounded by a Dehnen-type Dark Matter Halo
Shadows and Observational Images of a Schwarzschild-like Black Hole Surrounded by a Dehnen-type Dark Matter Halo
Zuting Luo, Meirong Tang, Zhaoyi Xu
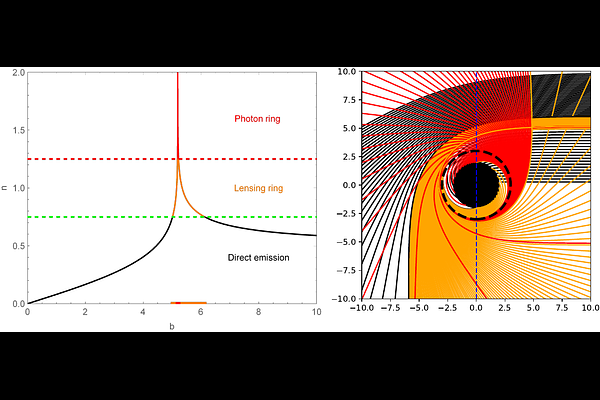
AbstractThis study investigates the optical appearance of a Schwarzschild-like black hole (BH) surrounded by a Dehnen-type dark matter (DM) halo, with a focus on how the DM halo's density $\rho_{s}$ and radius $r_{s}$ influence the BH's shadow and photon ring. First, the radius $r_h$ of the BH's event horizon and the equation of motion for photons were derived, and observational data from the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) for M87* were used to constrain the parameters $\rho_{s}$ and $r_{s}$ of the DM halo. Afterward, by varying the values of $\rho_{s}$ and $r_{s}$, key parameters such as the effective potential $V_{eff}$ of photons, the critical impact parameter $b_{ph}$, the radius $r_{isco}$ of the innermost stable circular orbit,and the the radius $r_{ph}$ of the photon sphere were calculated for each case. It was found that as $\rho_{s}$ and $r_{s}$ increase, the above mentioned parameters all show an increasing trend. Subsequently, we examined the optical appearance of the BH under two models: one with an optically and geometrically thin accretion disk and the other with a static spherical accretion model. The findings indicate that as $\rho_{s}$ and $r_{s}$ increase, the peak of the received intensity shifts toward a higher impact parameter $b$, resulting in a distinct optical appearance.