Notch Signaling in regulating Bone-derived Nanoparticles (BNPs) enhanced Osteogenic Differentiation
Notch Signaling in regulating Bone-derived Nanoparticles (BNPs) enhanced Osteogenic Differentiation
Wang, S.; Wang, B.; Stellpflug, A.; Caron, J.; Fasciano, S.
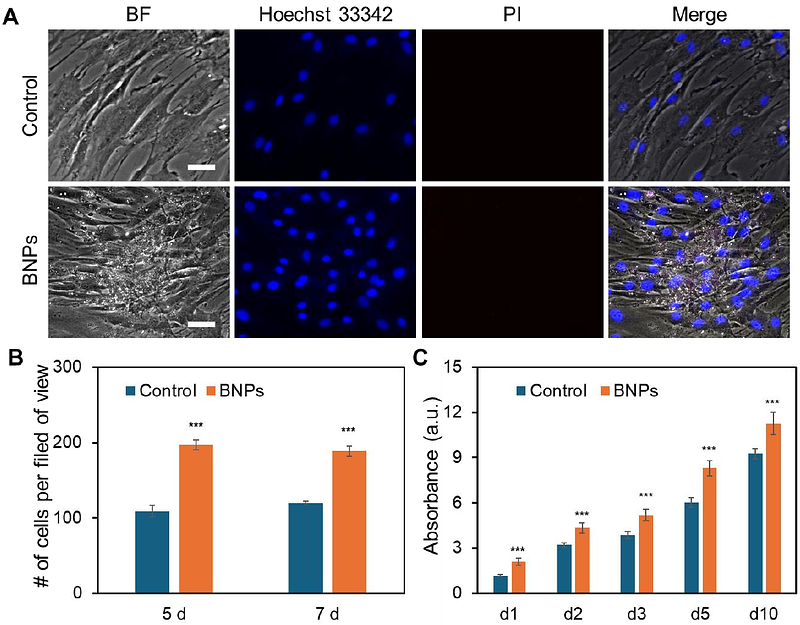
AbstractMesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)-based bone tissue regeneration has gained significant attention due to their excellent differentiation capacity and immunomodulatory activity. Enhancing osteogenesis regulation is crucial for improving the therapeutic efficacy of MSC-based regeneration. By utilizing the regenerative capacity of bone ECM and the functionality of nanoparticles, we recently engineered bone-based nanoparticles (BNPs) from decellularized porcine bone. The effects of internalization of BNPs on MSCs viability, proliferation, and osteogenic differentiation were first investigated and compared at different time points. The phenotypic behaviors, including cell number, proliferation, and differentiation were characterized and compared. By incorporating this LNA/DNA nanobiosensor and MSCs live cell imaging, we monitored and compared Notch ligand delta-like 4 (Dll4) expression dynamics in cytoplasm and nucleus during osteogenic differentiation. Pharmacological interventions are used to inhibit Notch signaling to examine the mechanisms involved. The results suggest Notch inhibition mediates osteogenic process, with reduced expression of early and late stage of differentiation markers (ALP, calcium mineralization). The internalization of BNPs led to an increase in Dll4 expression, exhibiting a time-dependent pattern that aligned with enhanced cell proliferation and differentiation. Our findings indicate that the observed changes in BNP-treated cells during osteogenic differentiation could be associated with the elevated levels of Dll4 mRNA expression. In summary, this study provides new insights into MSCs osteogenic differentiation and the molecular mechanisms through which BNPs stimulate this process. The results indicate that BNPs influence osteogenesis by modulating Notch ligand Dll4 expression, demonstrating a potential link between Notch signaling and the proteins present in BNPs.


