Data-driven feedback augments ultrasound nanotheranostics in brain tumors
Data-driven feedback augments ultrasound nanotheranostics in brain tumors
Lee, H.; Menezes, V.; Zeng, S.; Kim, C.; Baseman, C. M.; Kim, J. H.; Padmanabhan, S.; Premdas, P.; Djeddar, N.; Bryksin, A. V.; Pandey, N.; Anastasiadis, P.; Kim, A. J.; MacDonald, T. J.; Bettegowda, C.; Woodworth, G. F.; Hermann, F. J.; Arvanitis, C.
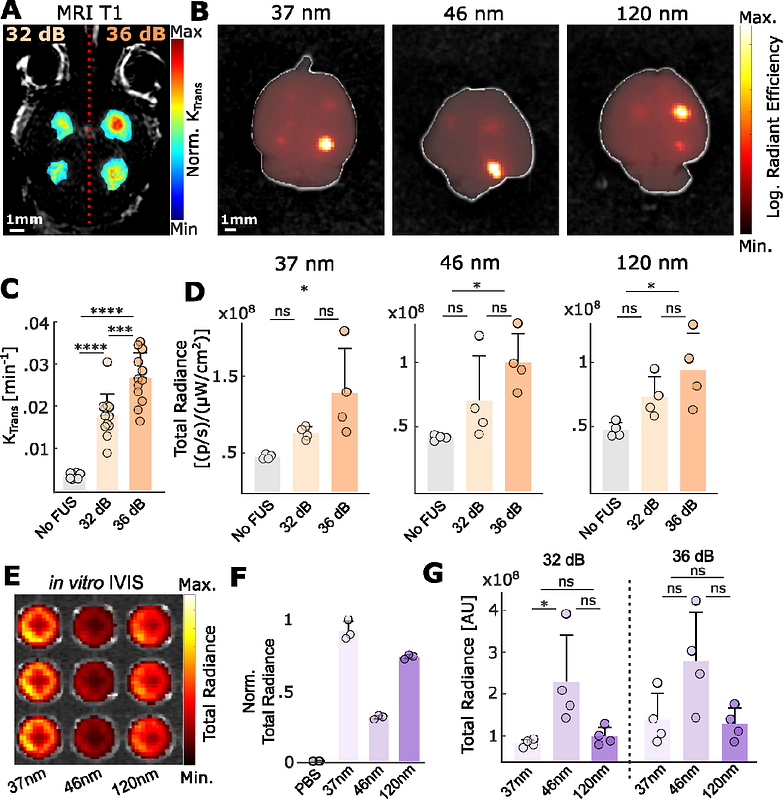
AbstractThe blood-brain barrier (BBB) renders the delivery of nanomedicine in the brain ineffective and the detection of circulating disease-related DNA from the brain unreliable. Here, we show that the acoustic emission content of focused ultrasound-controlled microbubble dynamics (MB-FUS) incorporates precursor signals that allow large-data models to predict sonication regimens for safe and effective BBB opening. Crucially, closed-loop MB-FUS controller augmented by machine learning (ML-CL) expands the treatment window (4-fold), as compared to conventional controllers, by persistently and proactively maximizing the BBB permeability while preventing tissue damage. By successfully scaling up from mice to rats and from healthy to diseased brains (glioma), ML-CL rendered the BBB permeable to large nanoparticles and markedly improved the release and detection of tumor DNA in plasma. Together, our findings reveal the potential of data-driven feedback to support the development of next-generation AI-powered ultrasound systems for safe, robust, and efficient nanotheranostic targeting of brain diseases.