Complete Enzyme Clustering Enhances Coenzyme Q Biosynthesisvia Substrate Channeling
Complete Enzyme Clustering Enhances Coenzyme Q Biosynthesisvia Substrate Channeling
Wang, D.; Gottinger, A.; Jeong, J.; Nicoll, C. R.; Liu, J.; Kadav, T.; Cecchini, D.; Malatesta, M.; Heck, A. J. R.; Mattevi, A.; Shakhnovich, E.
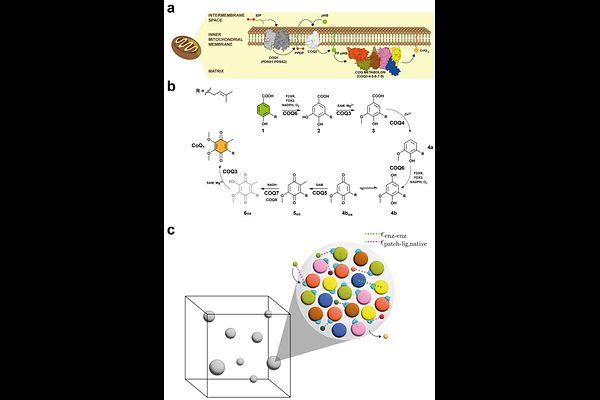
AbstractMetabolons - transient assemblies of sequential metabolic enzymes - facilitate the reactions of multi-step metabolic pathways, yet, how they mechanistically bolster metabolic flux remains unknown. Here, we investigate the molecular determinants of metabolon formation in coenzyme Q (CoQ) biosynthesis using coarse-grained molecular dynamics simulations and biochemical experiments. We show that the COQ metabolon forms at the critical region of a phase transition, where both metabolon clustering and metabolic flux exhibit coordinated sigmoidal responses to changes in protein-protein interaction strength. These complete metabolons enable substrate channeling between sequential enzymes, leading to a crucial enhancement of CoQ production efficiency. Selectively disrupting protein-protein interactions and randomly shuffling the interaction network demonstrate that protein-proximity rather than fine structure of the metabolon clusters is imperative for substrate channeling. Grounded in both experiment and simulation, these findings provide a framework for understanding the organization and function of metabolons across diverse metabolic pathways.