Highly Multiplexed Spatial Transcriptomics in Bacteria
Highly Multiplexed Spatial Transcriptomics in Bacteria
Sarfatis, A.; Wang, Y.; Twumasi-Ankrah, N.; Moffitt, J. R.
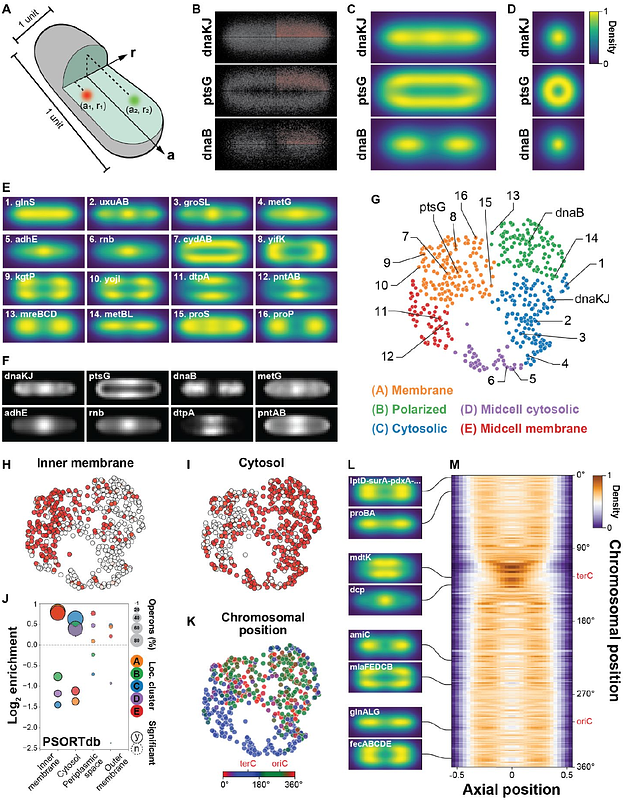
AbstractSingle-cell decisions made in complex environments underlie many bacterial phenomena. Image-based transcriptomics approaches offer an avenue to study such behaviors, yet these approaches have been hindered by the massive density of bacterial mRNA. To overcome this challenge, we combine 1000-fold volumetric expansion with multiplexed error robust fluorescence in situ hybridization (MERFISH) to create bacterial-MERFISH. This method enables high-throughput, spatially resolved profiling of thousands of operons within individual bacteria. Using bacterial-MERFISH, we dissect the response of E. coli to carbon starvation, systematically map subcellular RNA organization, and chart the adaptation of a gut commensal B. thetaiotaomicron to micron-scale niches in the mammalian colon. We envision bacterial-MERFISH will be broadly applicable to the study of bacterial single-cell heterogeneity in diverse, spatially structured, and native environments.