Immunomodulatory effect of HLA-G Overexpressed Mesenchymal Stromal Cell in Cell-based Therapy for Myocardial Infarction
Immunomodulatory effect of HLA-G Overexpressed Mesenchymal Stromal Cell in Cell-based Therapy for Myocardial Infarction
Sun, S.-J.; Zhu, W.; Kong, J.; Li, H.-X.; Jiang, T.; Zou, C.
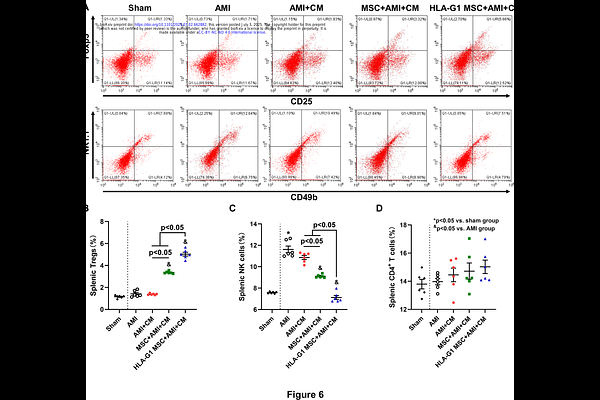
AbstractBackground: Our previous study demonstrated that intravenous administration of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) significantly increased local cell engraftment and improved heart function. We sought to investigate whether HLA-G1 overexpressed MSCs could further increase local transplanted cells engraftment and improve heart function. Methods and Results: Mice were randomized to receive intravenous administration of saline, human umbilical cord blood derived MSCs (hUCB-MSCs) 7 days prior to acute myocardial infarction (AMI), induced by ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery. Then, intramyocardial transplantation of human induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) was performed 30 minutes following AMI. Echocardiographic assessment was performed to assess heart function. In-vivo fluorescent imaging analysis were used to analyze cell engraftment. Flow cytometry of splenic regulatory T cells (Tregs) and natural killer (NK) cells was conducted to evaluate the immunomodulatory effect. Our result showed that systemic intravenous administration of hUCB-MSCs significantly increased systemic Tregs, decreased systemic NK cells, increased cell engraftment of intramyocardial transplanted hiPSC-CMs, culminating in improvement of heart function. Our in-vitro study showed that HLA-G1 overexpressed hUCB-MSCs modulated immune response by decreasing pro-inflammatory cytokines. Conclusions: Systemic intravenous administration of HLA-G1 overexpressed hUCB-MSCs modulated immune response and enhanced the survival of local transplanted hiPSC-CMs to improve heart function following AMI.