Genetic modifiers of somatic expansion and clinical phenotypes in Huntington's disease reveal shared and tissue-specific effects
Genetic modifiers of somatic expansion and clinical phenotypes in Huntington's disease reveal shared and tissue-specific effects
Genetic Modifiers of Huntington's Disease (GeM-HD) Consortium, ; Lee, J.-M.; McLean, Z. L.; Correia, K.; Shin, J. W.; Lee, S.; Jang, J.-H.; Lee, Y.; Kim, K.-H.; Choi, D. E.; Long, J. D.; Lucente, D.; Seong, I. S.; Mouro Pinto, R.; Giordano, J. V.; Mysore, J. S.; Jacqueline, S.; Elezi, E.; Ruliera, J.; Gillis, T.; Wheeler, V. C.; MacDonald, M. E.; Gusella, J. F.; Gatseva, A.; Ciosi, M.; Lomeikaite, V.; Loay, H.; Monckton, D. G.; Wills, C.; Massey, T. H.; Jones, L.; Holmans, P.; Kwak, S.; Sampaio, C.; Orth, M.; Landwehrmeyer, B.; Paulsen, J. S.; Dorsey, E. R.; Myers, R. H.
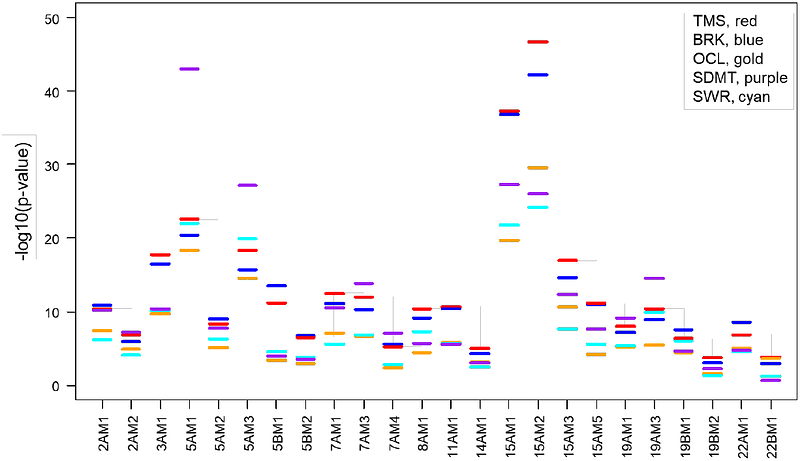
AbstractHuntington\'s disease (HD), due to expansion of a CAG repeat in HTT, is representative of a growing number of disorders involving somatically unstable short tandem repeats. We find that overlapping and distinct genetic modifiers of clinical landmarks and somatic expansion in blood DNA reveal an underlying complexity and cell-type specificity to the mismatch repair-related processes that influence disease timing. Differential capture of non-DNA-repair gene modifiers by multiple measures of cognitive and motor dysfunction argues additionally for cell-type specificity of pathogenic processes. Beyond trans modifiers, differential effects are also illustrated at HTT by a 5\'-UTR variant that promotes somatic expansion in blood without influencing clinical HD, while, even after correcting for uninterrupted CAG length, a synonymous sequence change at the end of the CAG repeat dramatically hastens onset of motor signs without increasing somatic expansion. Our findings are directly relevant to therapeutic suppression of somatic expansion in HD and related disorders and provide a route to define the individual neuronal cell types that contribute to different HD clinical phenotypes.


