T Lymphocyte-Specific Deletion of SHP1 and SHP2 Promotes Activation-Induced Cell Death of CD4+ T Cells and Impairs Antitumor Response
T Lymphocyte-Specific Deletion of SHP1 and SHP2 Promotes Activation-Induced Cell Death of CD4+ T Cells and Impairs Antitumor Response
Foster, C. J.; Du, J.; Pundel, O.; Geer, M. J.; Ripert, R. C.; Liu, J.; Heim, T. A.; Araki, K. Y.; Lund, A. W.; Wang, J.; Neel, B. G.
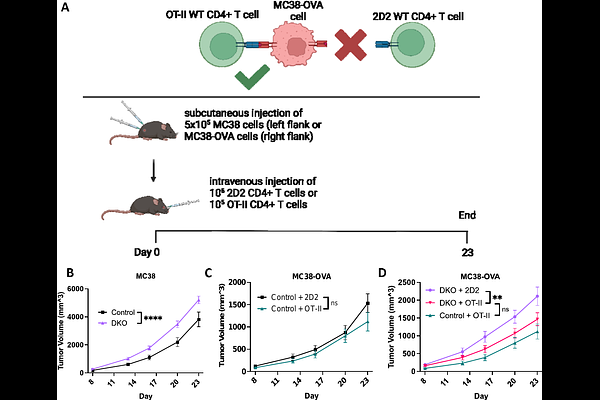
AbstractSHP1 (PTPN6) and SHP2 (PTPN11) are closely related protein-tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs), which are autoinhibited until their SH2 domains bind paired tyrosine-phosphorylated immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory/switch motifs (ITIMs/ITSMs). These PTPs bind overlapping sets of ITIM/ITSM-bearing proteins, suggesting that they might have some redundant functions. By studying T cell-specific single and double knockout mice, we found that SHP1 and SHP2 redundantly restrain naive T cell differentiation to effector and central memory phenotypes, with SHP1 playing the dominant role. Surprisingly, loss of SHP2 alone in T cells enhanced the antitumor effects of anti-PD-1 antibodies, whereas there was no effect of SHP1 deletion. Also unexpectedly, the absence of both PTPs resulted in poorer tumor control and failure to respond to PD-1 blockade, associated with reduced frequency and activation of T cells and dendritic cells. Mechanistic studies revealed that CD4+, but not CD8+ T cells lacking SHP1 and SHP2 show increased activation-induced cell death upon anti-CD3/CD28 stimulation. Adoptive transfer of antigen-specific CD4+ T cells restored normal levels of tumor control in mice lacking both PTPs. Together, our results demonstrate that SHP1 or SHP2 is required to prevent activation-induced cell death of CD4+ T cells and is critical for tumor immunity, raising the possibility that inhibition of SHP2 might augment the therapeutic efficacy of PD-1-based immune therapy.