Hippocampal Dipeptidyl Peptidase 9 Bilaterally Modulates Memory via its Enzymatic Activity
Hippocampal Dipeptidyl Peptidase 9 Bilaterally Modulates Memory via its Enzymatic Activity
Zhao, Y.-B.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Guo, W.; Xu, L.; Zhou, Q.-X.
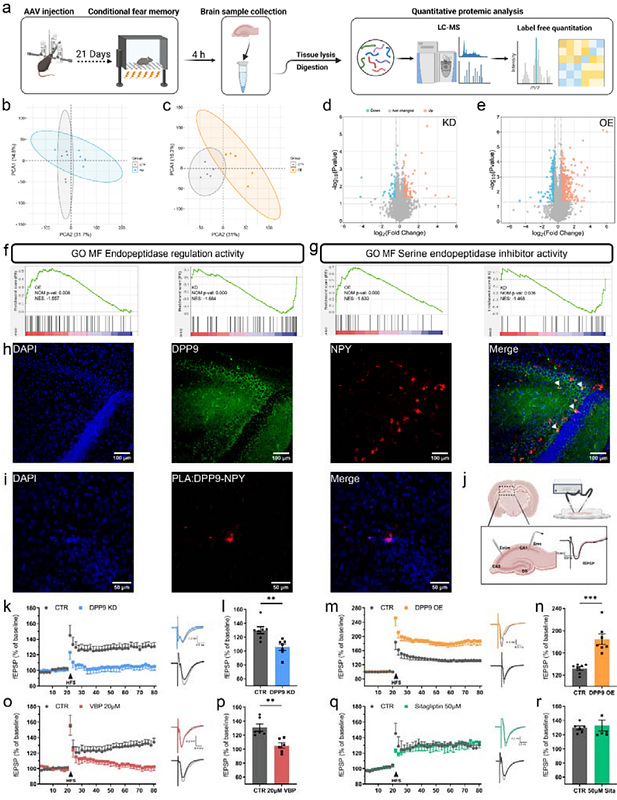
AbstractDipeptidyl peptidase 9 (DPP9) has been extensively studied for its role in inflammation and cancer. DPP9-interacting proteins and substrates are involved in brain functions such as neuroinflammation, learning and memory, and anxiety. However, the function of DPP9 in the central nervous system remains unknown. Here, we found that DPP9 is highly expressed in hippocampal neurons and plays a crucial role in long-term potentiation and memory by electrophysiological and behavioral experiments and immunofluorescence staining. Proteomics analysis identified differentially expressed proteins associated with memory retrieval regulated by DPP9. Further investigation revealed that DPP9 enzymatic activity is essential for memory consolidation. DPP9-interacting proteins are involved in dendritic spine and axon function, and two memory- and axon-related genes, Tmp3 and Baiap2, were identified as potential targets for DPP9. Our findings suggest that DPP9 is a novel memory regulatory protein and provide new insights into memory molecular mechanisms.