Multivalent Ligand-Protein Interactions Using Polymeric Lysosome-Targeting Chimeras (PolyTACs) Leads to Lysosome-Targeting Receptor-Independent Degradation of Transmembrane Proteins
Multivalent Ligand-Protein Interactions Using Polymeric Lysosome-Targeting Chimeras (PolyTACs) Leads to Lysosome-Targeting Receptor-Independent Degradation of Transmembrane Proteins
Dutta, R.; Alp, Y.; Gupta, P.; Singh, B.; Thayumanavan, S.
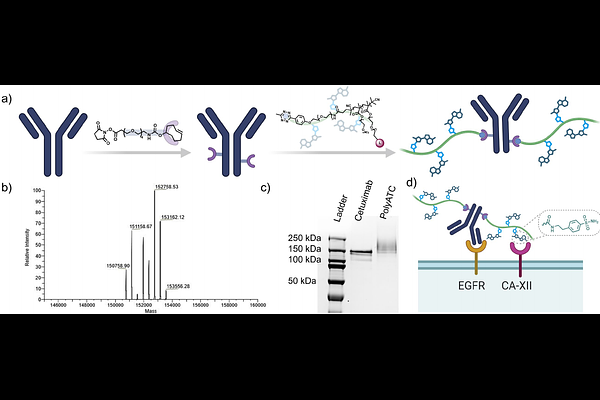
AbstractTargeted protein degradation is growing rapidly as a therapeutic approach, with intracellular proteins degraded via the ubiquitin-proteasome or the autophagosome system and membrane proteins mainly through the lysosomal pathway. Current lysosomal degradation strategies rely on lysosome-targeting receptors (LTRs), limiting their applicability. We propose that multivalent non-covalent interactions on the cell membrane can drive lysosomal degradation of membrane proteins without the need of LTRs. To demonstrate this, we designed antibody-polymer conjugates, viz. Polymeric Lysosome-Targeting Chimeras (PolyTACs) functionalized with ligands that would non-covalently bind with transmembrane non-LTR proteins, viz., helper proteins on the cell surface in a polyvalent fashion. Cetuximab-based PolyTACs decorated with 4-(2-aminoethyl)benzenesulfonamide (ABS) ligands that cause multivalent interactions with membrane carbonic anhydrases induced degradation of EGFR, while atezolizumab- and trastuzumab-based PolyTACs effectively degraded PD-L1 and HER2, respectively. Additionally, PolyTACs using PD-L1 as the helper protein further improved degradation. Mechanistic studies confirmed clathrin- and caveolae-mediated endocytosis followed by lysosomal degradation of the target proteins. This LTR-independent nature of the approach offers opportunities for tissues targeting in membrane protein degradation that could open up new avenues in therapeutic strategies.