A new family of statistical tests for responses in point-event and time-series data for one- and two-sample comparisons
A new family of statistical tests for responses in point-event and time-series data for one- and two-sample comparisons
Heimel, J. A.; Meijer, G. T.; Montijn, J. S.
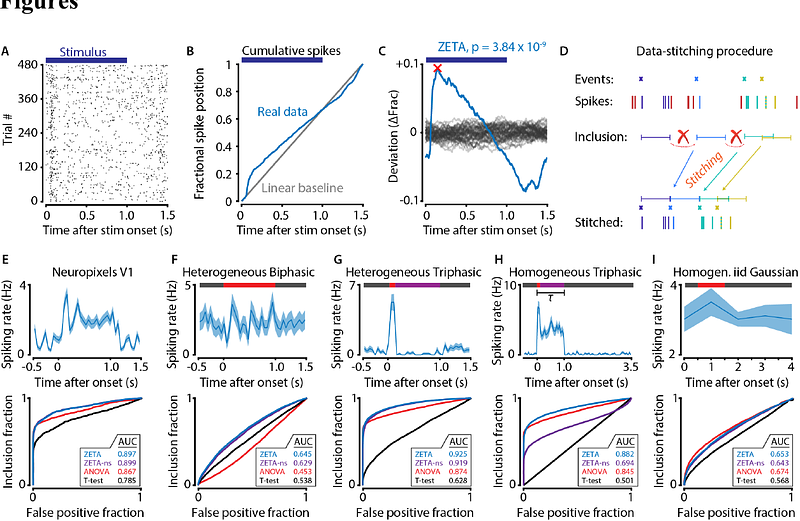
AbstractQuantifying whether and when signals are modulated by autonomous or external events is ubiquitous in the field of neuroscience. Existing statistical approaches, however, are not ideally suited to do this, especially when the signals under scrutiny show temporal autocorrelations. For example, a standard approach in the analysis of calcium imaging data is to use a t-test on predetermined time-windows to quantify whether neurons respond (differently) to an event of interest. While this is attractive because of its simplicity, only average signal differences can be detected. In practice, neurons often show complex response dynamics which are missed by conventional statistical tests. To solve this issue, we present an improved version of the recently developed ZETA-test which implements support for analysing time-series data. Furthermore, it includes a two-sample test to detect a difference in neural responses between two conditions. We show that our method has a statistical sensitivity superior to t-tests and ANOVAs and works well with temporally correlated data. Open-source code for implementations in MATLAB and Python is available on GitHub.