Traitor-virus-guided discovery of novel antiviral factors
Traitor-virus-guided discovery of novel antiviral factors
Prelli Bozzo, C.; Laliberte, A.; De Luna, A.; Pastorio, C.; Regensburger, K.; Krebs, S.; Graf, A.; Blum, H.; Volcic, M.; Sparrer, K. M.; Kirchhoff, F.
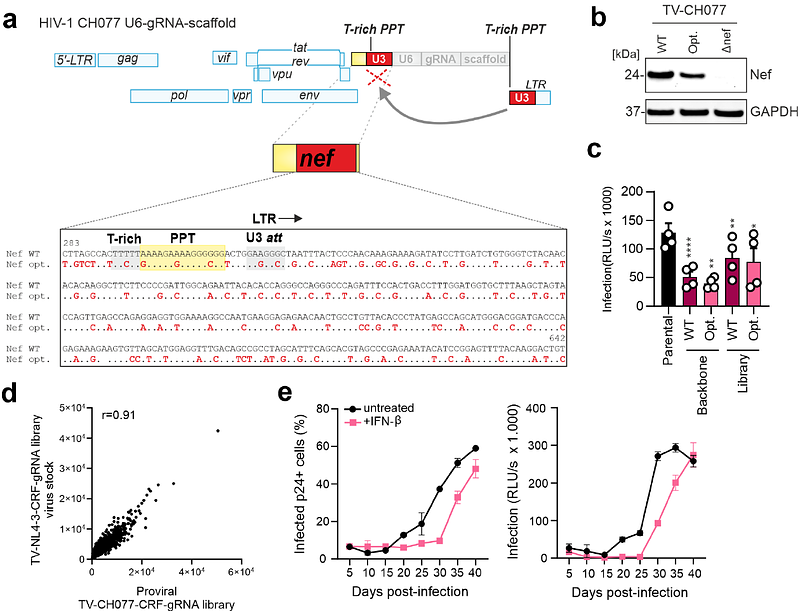
AbstractComplex pathogen-host interactions govern the outcome of viral exposures but remain poorly understood because current methods to elucidate antiviral mechanisms are prone to artefacts and lack sensitivity. Here, we developed a virus-guided technology platform where the pathogen itself reveals its cellular opponents. To accomplish this, we engineered replication-competent HIV-1 expressing sgRNAs targeting potential antiviral genes in Cas9-expressing CD4+ T cells. Simultaneous analysis of HIV-1 constructs targeting >500 candidate genes revealed that sgRNAs against GRN, CIITA, EHMT2, CEACAM3, CC2D1B, RHOA and HMOX1 are strongly enriched over several rounds of replication. Overexpression and knock-out studies confirmed the antiretroviral activity of most factors but failed for some. Finally, we show that lack of the accessory nef gene increased enrichment of sgRNAs targeting SERINC5 and IFI16 demonstrating that this method allows identification of targets of accessory proteins. The versatile and effective HIV-guided CRISPR technology offers numerous possibilities for clarification of virus-host interactions and innate defense mechanisms.