Lipid nanoparticle delivered intrabodies for inhibiting necroptosis and pyroptosis
Lipid nanoparticle delivered intrabodies for inhibiting necroptosis and pyroptosis
Deepagan, V. G.; Ma, X.; Bazregari, F.; Pang, J.; Schaefer, J.; Hildebrand, J. M.; Dempsey, R. K.; Doerflinger, M.; Baldwin, C. A.; Schmidt, F. I.; Murphy, J. M.; Salvamoser, R.; Vince, J. E.
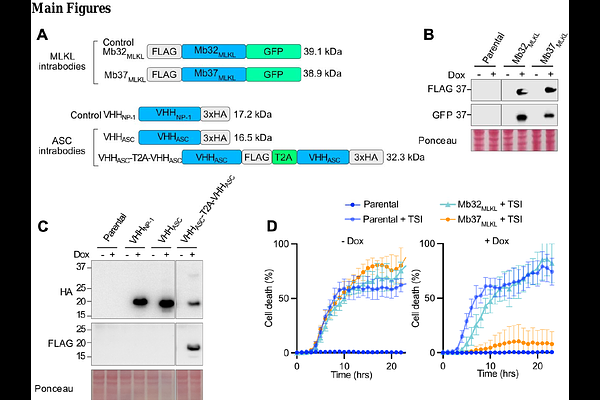
AbstractIntrabodies are intracellularly expressed high-affinity protein binders such as nanobodies and monobodies that offer an alternative approach to small molecules. However, the maturation of intrabody technology into new therapeutic modalities has been limited by the availability of a clinically relevant delivery system enabling sufficiently high levels of protein to be expressed in the cytosol. Here, we use lipid nanoparticle (LNP) systems based on clinically approved formulations for the efficient intracellular delivery of mRNAs encoding for intrabodies targeting mixed lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase (MLKL) and apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD (ASC), key mediators of the necrotic cell death modalities, necroptosis and pyroptosis, respectively. LNP delivery of intrabody mRNA resulted in robust protein expression, with a MLKL binding intrabody preventing MLKL membrane translocation and protecting against necroptotic cell death. Similarly, LNP delivery of a bivalent intrabody targeting the inflammasome adaptor protein ASC protected against NLRP3 and AIM2 inflammasome-driven responses, including caspase-1 and IL-1beta activation and gasdermin D-driven pyroptotic killing. These findings establish that LNPs harbouring anti-necrotic intrabody mRNAs allow for sufficient intracellular expression to neutralize necrotic cell death signalling and provide a general, clinically relevant, strategy for delivering therapeutic intrabodies into cells.