A lipid metabolism defect is an underlying contributor to Diamond Blackfan anemia syndrome
A lipid metabolism defect is an underlying contributor to Diamond Blackfan anemia syndrome
Deng, K.; Wang, Y.; Mic, J. C.; Liu, X.; Myers, G.; Yu, L.; Hammoud, S.; Adam, A.; Saba, R.; Natogi, V.; Drysdale, C.; Chen, B.; Ueharu, H.; Yee, J. L.; Kitzman, J.; Lyssiotis, C. A.; Mishina, Y.; Jones, M.; Kaartinen, V.; Guan, Y.; Khoriaty, R.; Engel, J. D.; Singh, S. A.
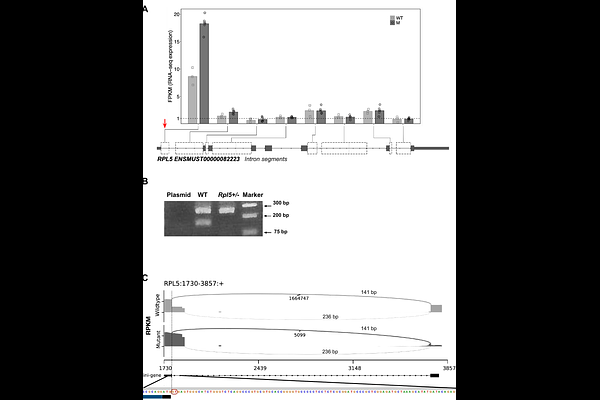
AbstractAnalysis of neither Diamond Blackfan anemia syndrome (DBAS) cohorts nor animal models has revealed a potential mechanism for the variable anemia phenotype, a key feature of this disease. Here, we utilized an established Rpl5Skax23-Jus/+ murine DBAS model in order to study this dynamic erythropoiesis deficiency. These haploinsufficient mice exhibit variably penetrant craniofacial and cardiac defects mimicking the phenotypes of DBAS patients bearing RPL5 mutations. We additionally discovered that this specific heterozygous splicing mutation is pathogenic and leads to intron retention. By examining the transcriptome of fetal liver erythroid progenitors at E12.5, we demonstrate that the downregulation of erythroid differentiation pathways is consistent with the DBAS phenotype. We also identified dysregulation of lipid metabolism genes with significant reduction in the abundance of Scd1 in a subset of E12.5 mutant embryos at risk for erythroid failure. SCD1, a key enzyme that converts saturated to monounsaturated fatty acids, has not been previously linked to erythropoiesis or DBAS. When anemia was induced in adult mice, pretreatment with an SCD1 inhibitor resulted in improved erythropoiesis. This analysis suggests a key role of lipid metabolism in the variable anemia penetrance in DBAS and highlights a previously unappreciated pathway that may serve as a potential target for drug development.