Compensation of Hyperexcitability with Simulation-Based Inference
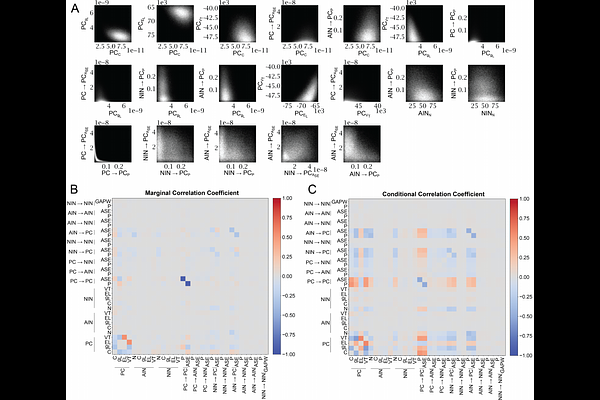
Compensation of Hyperexcitability with Simulation-Based Inference
Mueller-Komorowska, D.; Fukai, T.
AbstractThe activity of healthy neuronal networks is tightly regulated, and a shift towards hyperexcitability can cause various problems, such as epilepsies, memory deficits, and motor disorders. Numerous cellular, synaptic, and intrinsic mechanisms of hyperexcitability and compensatory mechanisms to restore healthy activity have been proposed. However, quantifying multiple compensatory mechanisms and their dependence on specific pathophysiological mechanisms has proven challenging, even in computational models. We use simulation-based inference to quantify the interactions of compensatory mechanisms in a spiking neuronal network model. Various parameters of the model can compensate for changes in other parameters to maintain baseline activity, and we rank them by their compensatory potential. Furthermore, specific causes of hyperexcitability - interneuron loss, excitatory recurrent synapses, and principal cell depolarization - have distinct compensatory mechanisms that can restore normal excitability. Our results show that spiking neuronal network simulators could provide the quantitative foundation for targeting pathophysiological network mechanisms with precise interventions.