Detection of Diffuse to Focal Myocardial Fibrosis by Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Against Histology in Mini-Swine
Detection of Diffuse to Focal Myocardial Fibrosis by Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Against Histology in Mini-Swine
Zhang, H.; Cui, C.; Yang, W.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Piechnik, S. K.; Ferreira, V. M.; Lu, M.
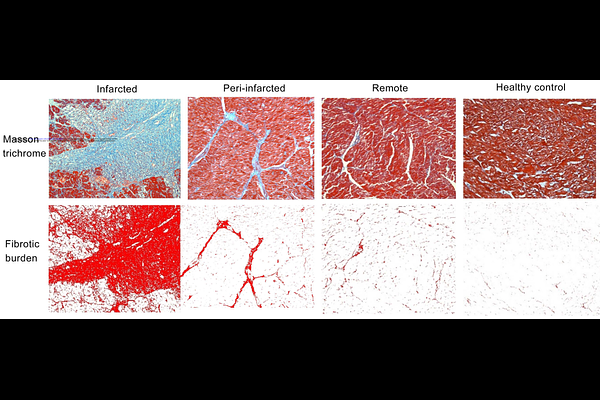
AbstractBackground: Myocardial fibrosis predicts adverse outcomes in myocardial infarction (MI) and other cardiovascular conditions. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) can non-invasively detect focal and diffuse myocardial fibrosis, but comprehensive validation against histology remains scarce. Aims: To assess the comparative diagnostic performance of CMR methods in detecting myocardial fibrosis, using a mini-swine model and histology as gold standard. Methods: Eighteen mini-swine (16 MI; 2 healthy) underwent CMR cine, LGE, T1- and ECV-mapping. Two commonly-used T1-mapping methods - MOLLI 5(3)3 and ShMOLLI 5(1)1(1)1 - were included. Pathological sections were categorized as infarcted, peri-infarct, remote and healthy myocardium based on triphenyl tetrazolium chloride staining. Fibrotic burden was quantified by collagen volume fraction (CVF) into severe (CVF?30%), moderate (CVF=10-25%), and mild (CVF=3-14%). The relationships between LGE, T1, ECV and CVF, and diagnostic performance using area-under-the-curve (AUC), were analyzed. Results: For detecting severe fibrosis, LGE, T1 and ECV all had excellent diagnostic performance (AUC: LGE=0.93, ECVShMOLLI=0.96, T1ShMOLLI=0.91, T1MOLLI=0.93, ECVMOLLI=0.88). ECVShMOLLI showed significantly better discriminatory accuracy than ECVMOLLI in detecting severe fibrosis and MI (both p<0.05), with the highest correlation to CVF (ECVShMOLLI r=0.86, ECVMOLLI r=0.82, T1ShMOLLI r=0.77, T1MOLLI r=0.77, semi-quantitative LGE r=0.75). Only T1ShMOLLI and ECVShMOLLI, but not LGE or T1MOLLI/ECVMOLLI, differentiated remote myocardium with mild fibrosis (CVF=8.23%) from healthy myocardium (CVF=2.01%). Conclusions: CMR can detect severe to mild myocardial fibrosis as validated against histology. For low-grade fibrosis, T1-mapping significantly outperformed LGE. Choice of CMR methodologies matters for myocardial fibrosis detection, which has importance for clinical trial design.