Excessive cortical beta oscillations are associated with slow-wave sleep dysfunction in mild parkinsonism
Voice is AI-generated
Connected to paperThis paper is a preprint and has not been certified by peer review
Excessive cortical beta oscillations are associated with slow-wave sleep dysfunction in mild parkinsonism
Verma, A. K.; Nandakumar, B.; Acedillo, K.; Yu, Y.; Marshall, E.; Schneck, D.; Fiecas, M.; Wang, J.; MacKinnon, C. D.; Howell, M. J.; Vitek, J. L.; Johnson, L. A.
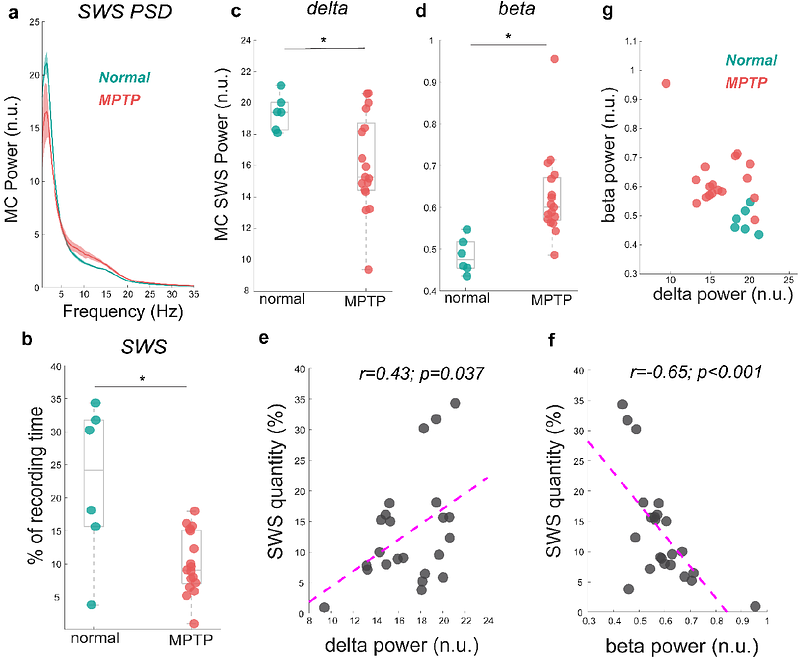
AbstractIncreasing evidence associates slow-wave sleep (SWS) dysfunction with neurodegeneration. Using a within-subject design in the nonhuman primate model of Parkinson\'s disease (PD), we found that reduced SWS quantity in mild parkinsonism was accompanied by elevated beta and reduced delta power during SWS in the motor cortex. Our findings support excessive beta oscillations as a mechanism for SWS dysfunction and will inform development of neuromodulation therapies for enhancing SWS in PD.