Whole-body coarticulation reflects expertise in sport climbing
Whole-body coarticulation reflects expertise in sport climbing
Maselli, A.; Musculus, L.; Moretti, R.; d'Avella, A.; Raab, M.; Pezzulo, G.
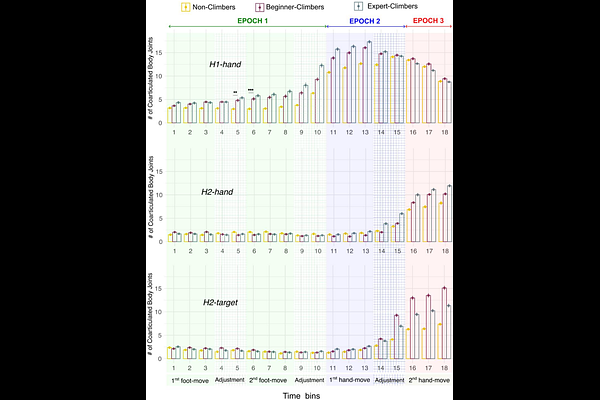
AbstractTaking sport climbing as a testbed, we explored coarticulation in naturalistic motor-behavior at the level of whole-body kinematics. Participants were instructed to execute a series of climbing routes, each composed of two initial foot-moves equal in all routes, and two subsequent hand-moves differing across routes in a set of eight possible configurations. The goal was assessing whether climbers modulate the execution of a given move depending on which moves come next in the plan. Coarticulation was assessed by training a set of classifiers and estimating how well the whole-body (or single-joint) kinematics during a given stage of the climbing execution could predict its future unfolding. Results showed that most participants engage in coarticulation, with temporal and bodily patterns that depend on expertise. Non-climbers tend to prepare the next-to-come move right before its onset and only after the end of the previous move. Rather, expert-climbers (and to a smaller extent, beginner-climbers) show early coarticulation during the execution of the previous move and engage in adjustments that involve the coordination of a larger number of joints across the body. These results demonstrate coarticulation effects in whole-body naturalistic motor behavior and as a function of expertise. Furthermore, the enhanced coarticulation found in expert-climbers provides hints for experts engaging in more refined mental processes converting abstract instructions (e.g., move the right hand to a given location) into motor simulations involving whole-body coordination. Overall, these results contribute to advancing our current knowledge of the rich interplay between cognition and motor control.