In vivo evolution of Candida auris multi-drug resistance in a patient receiving antifungal treatment
In vivo evolution of Candida auris multi-drug resistance in a patient receiving antifungal treatment
Wang, T. W.; Putnam, N.; Johnson, J. K.; Jabra-Rizk, M. A.
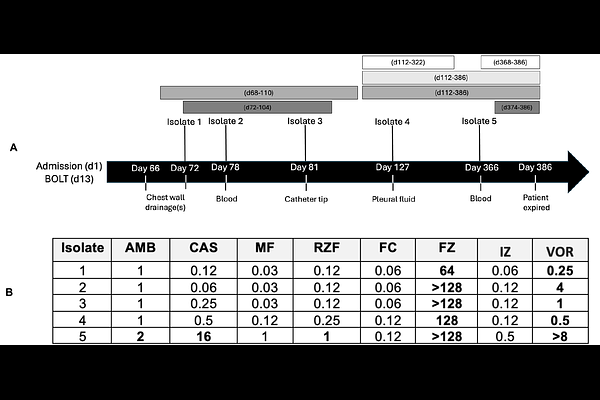
AbstractCandida auris is associated with life-threatening invasive disease due to high level of drug resistance. We present a clinical case of C. auris multi-drug resistance development in a single patient acquired during antifungal treatment. Five isolates were prospectively recovered from a transplant patient receiving antifungal therapy over a one-year period. While isolates were initially only resistant to fluconazole, the terminal isolate became resistant to caspofungin and amphotericin B with significant increase in micafungin MIC. Sequencing of ERG11 and FKS1 genes identified mutations associated with fluconazole and echinocandin resistance in the multi-drug-resistant isolate, underscoring the threat of therapy-induced development of resistance.