Loss of TMEM106B exacerbates Tau pathology and neurodegeneration in PS19 mice
Loss of TMEM106B exacerbates Tau pathology and neurodegeneration in PS19 mice
Feng, T.; Du, H.; Hu, F.
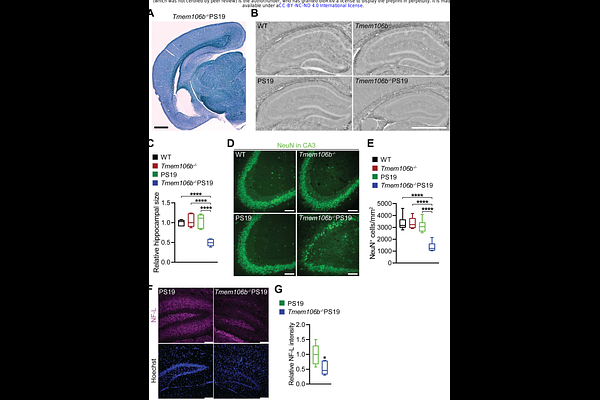
AbstractTMEM106B, a gene encoding a lysosome membrane protein, is tightly associated with brain aging, hypomyelinating leukodystrophy, and multiple neurodegenerative diseases, including frontotemporal lobar degeneration with TDP-43 aggregates (FTLD-TDP). Recently, TMEM106B polymorphisms have been associated with tauopathy in chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) and FTLD-TDP patients. However, how TMEM106B influences Tau pathology and its associated neurodegeneration, is unclear. Here we show that loss of TMEM106B enhances the accumulation of pathological Tau, especially in the neuronal soma in the hippocampus, resulting in severe neuronal loss in the PS19 Tau transgenic mice. Moreover, Tmem106b-/- PS19 mice develop significantly increased disruption of the neuronal cytoskeleton, autophagy-lysosomal function, and lysosomal trafficking along the axon as well as enhanced gliosis compared with PS19 and Tmem106b-/- mice. Together, our findings demonstrate that loss of TMEM106B drastically exacerbates Tau pathology and its associated disease phenotypes, and provide new insights into the roles of TMEM106B in neurodegenerative diseases.