Gravitational waves from b-EMRIs: Doppler shift and beaming, resonant excitation, helicity oscillations and self-lensing
Gravitational waves from b-EMRIs: Doppler shift and beaming, resonant excitation, helicity oscillations and self-lensing
João S. Santos, Vitor Cardoso, José Natário, Maarten van de Meent
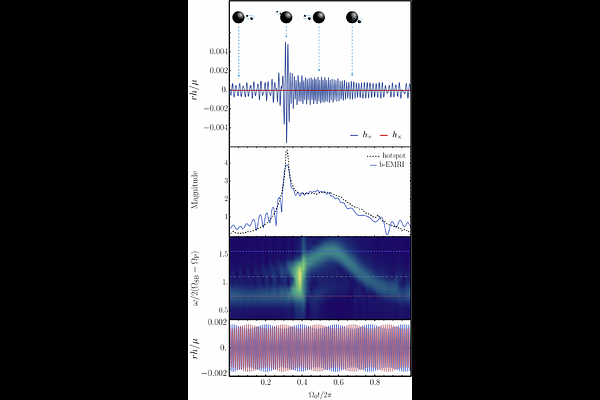
AbstractWe study gravitational waves from a stellar-mass binary orbiting a spinning supermassive black hole, a system referred to as a binary extreme mass ratio inspiral (b-EMRI). We use Dixon's formalism to describe the stellar-mass binary as a particle with internal structure, and keep terms up to quadrupole order to capture the generation of gravitational waves by the inner motion of the stellar-mass binary. The problem of emission and propagation of waves is treated from first principles using black hole perturbation theory. In the gravitational waveform at future null infinity, we identify for the first time Doppler shifts and beaming due to the motion of the center of mass, as well as helicity breaking gravitational lensing, and resonances with ringdown modes of the supermassive black hole. We establish that previously proposed phenomenological models inadequately capture these effects.