A GCN1-independent activator of the kinase GCN2
A GCN1-independent activator of the kinase GCN2
Zhu, J.; Emanuelli, G.; Masson, G.; Vinciauskaite, V.; Willems, H.; Lim, A.; Brown, C. A.; Winpenny, D.; Clarke, M.; Gilley, R.; Preston, F.; Wilson, J.; Bader, A.; Rahman, T.; Chambers, J. E.; Skidmore, J.; Morrell, N.; Marciniak, S. J.
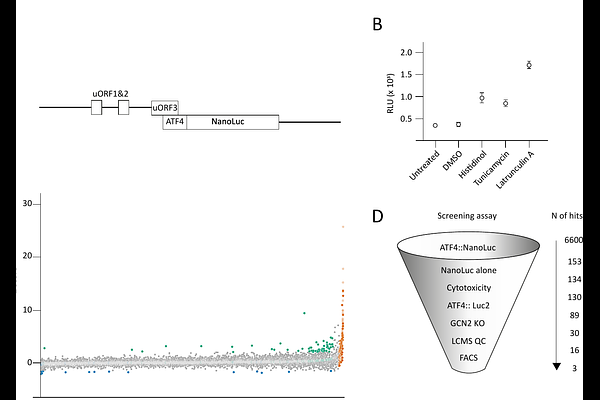
AbstractMutations of EIF2AK4, which encodes the eIF2alpha; kinase GCN2, cause a severe inherited form of pulmonary hypertension called pulmonary veno-occlusive disease (PVOD). Some pathogenic variants of GCN2 are amenable to pharmacological reactivation by low concentrations of ATP-pocket binding inhibitors. Kinase inhibition at modestly elevated concentrations limits the clinical utility of these drugs against PVOD. We therefore performed an in cellulo chemical screen for GCN2 activators and identified three structurally distinct compounds with low micromolar stimulatory activities. Unlike previously described GCN2 activators, one of these molecules activated GCN2 independently of GCN1. Modelling supported by structure activity screens suggested it binds within the ATP-pocket of GCN2, but unlike existing ligands does not protrude inward into the allosteric pocket or outward into the solvent. This overcomes a key requirement of other GCN2 activators.