Unmasking Human T Cell Receptor Germline Diversity: 335 Novel Alleles Identified in 47 Pangenome Reference Individuals Using the gAIRR Suite
Unmasking Human T Cell Receptor Germline Diversity: 335 Novel Alleles Identified in 47 Pangenome Reference Individuals Using the gAIRR Suite
Yang, Y.-H.; Yao, C.-Y.; Lin, M.-J.; Huang, K.-T.; Lin, Y.-H.; Chiu, I.-H. C.; Lai, S.-K.; Chen, C.-Y.; Yang, Y.-C.; Hsu, C.-L.; Hsu, J. S.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chen, P.-L.
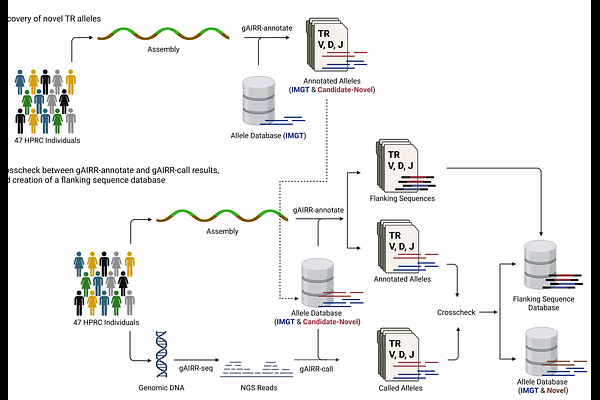
AbstractThe adaptive immune receptor repertoire (AIRR), composed of V(D)J-recombined T cell receptors (TR) and immunoglobulins (IG), is central to adaptive immunity. Accurate AIRR profiling depends on a comprehensive and diverse germline gene set encoding AIRR (gAIRR). Furthermore, gAIRR alleles themselves are associated with immune-related phenotypes and diseases. However, for TR genes, the IMGT database - the primary gAIRR reference - has not been updated since 2020 and lacks sufficient population diversity and complete flanking sequences. To address these limitations, we investigated 47 high-quality genomes from the Human Pangenome Reference Consortium (HPRC) using the gAIRR Suite and identified 335 novel TR alleles - 305 TRV and 30 TRJ - representing 91.6% and 30.9% increases over IMGT records. All novel alleles were crosschecked using two orthogonal pipelines. We also established a comprehensive flanking sequence database, including recombination signal sequences (RSS). We have made all resources publicly available to support immunogenomics research and clinical applications.