In vivo tracking of CAR-T cells in tumors via nanobubble-based contrastenhanced ultrasound
In vivo tracking of CAR-T cells in tumors via nanobubble-based contrastenhanced ultrasound
Durig, D.; Franklin, J.; Perera, R.; Jackson, Z.; Vasanna, H.; Kolios, M.; Wald, D.; Exner, A. A.
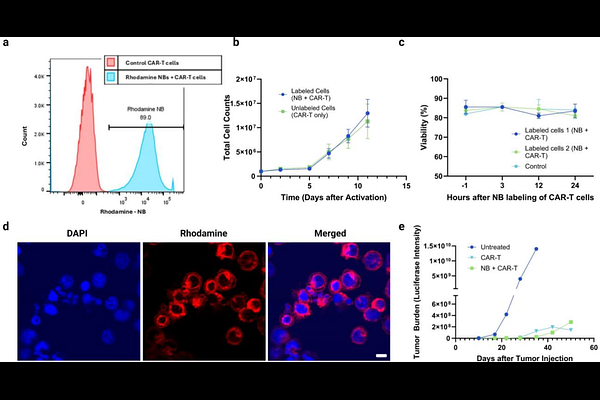
AbstractThis study demonstrates a novel concept in nanomedicine: the feasibility of non-invasively tracking CAR-T cells using nanosized ultrasound contrast agents. This innovative approach addresses critical challenges in understanding CAR-T cell infiltration and localization within solid tumor environments. Unlike existing methods for non-invasive CAR-T cell tracking, which are often limited by high costs, restricted accessibility, reduced cell viability, or reliance on radiation exposure, our method leverages nanobubbles combined with ultrasound to offer a cost-effective, safe, and widely accessible alternative. By utilizing nanobubble internalization in CAR-T cells, this research establishes an innovative method for ultrasound-based immune cell tracking. It offers valuable insights into the potential of nanotechnology to improve CAR-T cell therapy, particularly in overcoming the challenges associated with treating solid tumors. These findings contribute to the field of materials science by showcasing how nanoscale engineering can enable practical and clinically relevant solutions in immune cell tracking and therapy.