Single Nucleus RNA Sequencing of Remnant Kidney Biopsies and Urine Cell RNA Sequencing Reveal Cell Specific Markers of Covid-19 Acute Kidney Injury
Single Nucleus RNA Sequencing of Remnant Kidney Biopsies and Urine Cell RNA Sequencing Reveal Cell Specific Markers of Covid-19 Acute Kidney Injury
Ghag, R.; Kaushal, M.; Nwanne, G.; Knoten, A.; Kiryluk, K.; Rosenberg, A.; Menez, S.; Bagnasco, S. M.; Sperati, C. J.; Atta, M. G.; Gaut, J. P.; Williams, J. C.; El-Achkar, T. M.; Arend, L. J.; Parikh, C. R.; Jain, S.
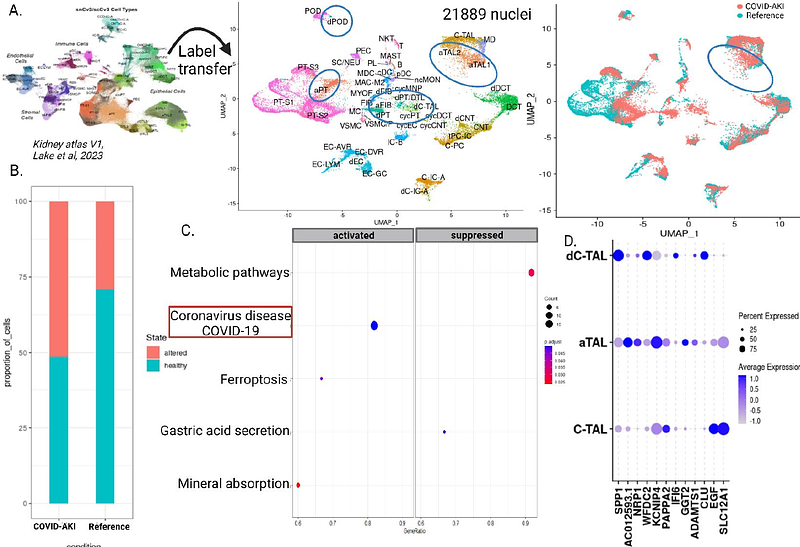
AbstractAcute kidney injury (AKI) in COVID-19 patients is associated with high mortality and morbidity. Critically ill COVID-19 patients are at twice the risk of in-hospital mortality compared to non-COVID AKI patients. We know little about the cell-specific mechanism in the kidney that contribute to worse clinical outcomes in these patients. New generation single cell technologies have the potential to provide insights into physiological states and molecular mechanisms in COVID-AKI. One of the key limitations is that these patients are severely ill posing significant risks in procuring additional biopsy tissue. We recently generated single nucleus RNA-sequencing data using COVID-AKI patient biopsy tissue as part of the human kidney atlas. Here we describe this approach in detail and report deeper comparative analysis of snRNAseq of 4 COVID-AKI, 4 reference, and 6 non-COVID-AKI biopsies. We also generated and analyzed urine transcriptomics data to find overlapping COVID-AKI-enriched genes and their corresponding cell types in the kidney from snRNA-seq data. We identified all major and minor cell types and states by using by using less than a few cubic millimeters of leftover tissue after pathological workup in our approach. Differential expression analysis of COVID-AKI biopsies showed pathways enriched in viral response, WNT signaling, kidney development, and cytokines in several nephron epithelial cells. COVID-AKI profiles showed a much higher proportion of altered TAL cells than non-COVID AKI and the reference samples. In addition to kidney injury and fibrosis markers indicating robust remodeling we found that, 17 genes overlap between urine cell COVID-AKI transcriptome and the snRNA-seq data from COVID-AKI biopsies. A key feature was that several of the distal nephron and collecting system cell types express these markers. Some of these markers have been previously observed in COVID-19 studies suggesting a common mechanism of injury and potentially the kidney as one of the sources of soluble factors with a potential role in disease progression.