Design and development of lysyl tRNA synthetase inhibitors, for the treatment of tuberculosis
Design and development of lysyl tRNA synthetase inhibitors, for the treatment of tuberculosis
Davis, S. H.; Mathieson, M.; Buchanan, K. I.; Dawson, A.; Smith, A.; Cocco, M.; Tamaki, F. K.; Post, J.; Baragana, B.; Jansen, C.; Kiczun, M.; Zuccotto, F.; Wood, G.; Scullion, P.; Ray, P. C.; Epemolu, O.; Lopez-Roman, E. M.; Guijarro Lopez, L.; Engelhart, C. A.; Kim, J.; Pino, P. A.; Schnappinger, D.; Read, K. D.; Encinas, L.; Bates, R. H.; Wyatt, P. G.; Green, S. R.; Cleghorn, L. A.
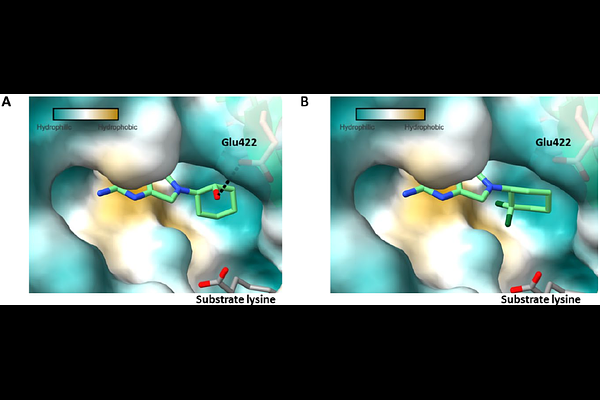
AbstractThere is currently a public health crisis due to the rise of multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis cases, as well as the rise in number of deaths from tuberculosis. To achieve the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal of ending the tuberculosis epidemic by 2030, new treatments are urgently required. We previously reported the discovery of 49, a pre-clinical candidate that acted through inhibition of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis lysyl-tRNA synthetase (LysRS). In this report, the full medicinal chemistry program is reviewed from the original hit through to the optimised lead. The work was guided by the first crystal structure of M. tuberculosis LysRS. The physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties were optimised to afford compounds suitable for evaluation in mouse efficacy models of tuberculosis and with the potential for clinical development.