A New Model of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction Induced by Metabolic Syndrome in Ossabaw Miniature Swine
A New Model of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction Induced by Metabolic Syndrome in Ossabaw Miniature Swine
Tang, X.-L.; Alloosh, M.; Ou, Q.; Luo, L.; Agrawal, D. K.; Kalra, D. K.; Sturek, M.; Bolli, R.
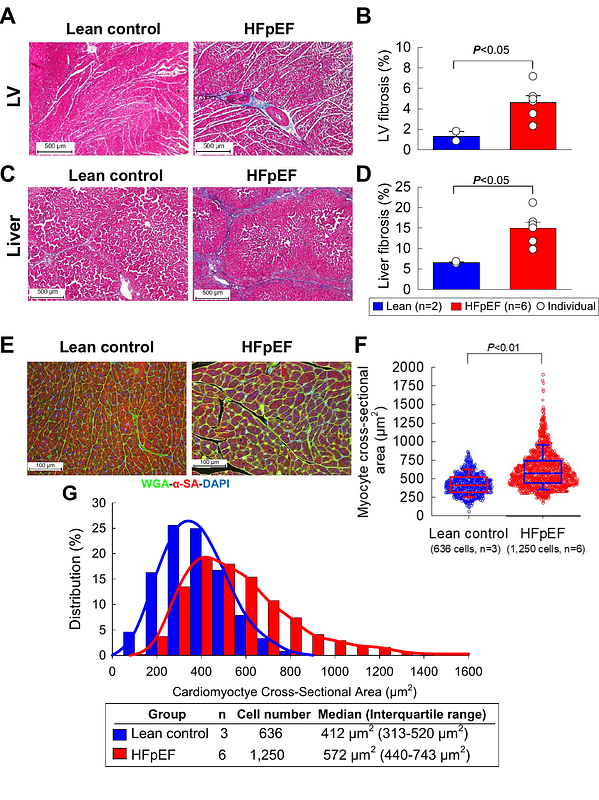
AbstractA major obstacle to progress in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is the paucity of clinically relevant animal models. We developed a large, translationally relevant model in Ossabaw minipigs, which are genetically predisposed to the metabolic syndrome (MetS). Pigs were fed a Western diet high in calories, fructose, fat, cholesterol, and salt and received 1-2 deoxy-corticosterone acetate (DOCA) depots (n=10). After 6 months, they exhibited liver function abnormalities and marked increases in body weight, arterial blood pressure, serum cholesterol and triglycerides, and plasma glucose and insulin levels (glucose tolerance test), indicating the development of a full MetS. Echocardiography demonstrated no change in LV ejection fraction but progressive concentric LV hypertrophy and left atrial dilatation. Doppler echocardiography showed increased E/e ratio and increased peak early (E) and peak late atrial (A) transmitral inflow velocities, with no change in E/A ratio. Right heart catheterization demonstrated increased central venous pressure, pulmonary arterial systolic pressure, and pulmonary capillary wedge pressure. Clinically, pigs exhibited impaired exercise capacity, assessed by treadmill tests, associated with chronotropic incompetence. Pathologic examination showed significant myocardial fibrosis, myocyte hypertrophy, and liver fibrosis. In contrast, lean pigs fed a standard diet (n=3) did not show any changes at 6 months. The Ossabaw porcine model described herein is unique in that it recapitulates the entire constellation of major multiorgan comorbidities and hemodynamic, clinical, and metabolic features of MetS-driven human HFpEF: obesity, arterial hypertension, hyperlipidemia, glucose intolerance, insulin resistance, liver fibrosis and dysfunction, pulmonary hypertension, increased LV filling pressures, concentric LV hypertrophy, LV diastolic dysfunction with preserved systolic function, and impaired exercise capacity. Because of its high clinical relevance, this model is well-suited for exploring the pathophysiology of MetS-driven HFpEF and the efficacy of new therapies.