Identification and biosynthesis of xildivaline, a novel and widespread peptide deformylase inhibitor from Gammaproteobacteria
Identification and biosynthesis of xildivaline, a novel and widespread peptide deformylase inhibitor from Gammaproteobacteria
Rill, A.; Westphalen, M.; Lamberioux, M.; Chekaiban, J.; Janin, C.; Mazel, D.; Groll, M.; Huber, E. M.; Bode, H. B.
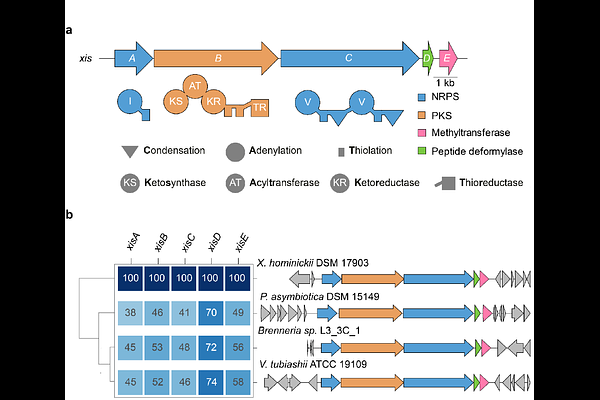
AbstractXenorhabdus strains, Gram-negative bacteria pathogenic to insects and symbionts to nematodes of the genus Steinernema are prolific producers of various natural products. Here we describe the xisABCDE biosynthesis gene cluster from Xenorhabdus hominickii responsible for the production of xildivalines. These non-ribosomal peptide and polyketide hybrids act as peptide deformylase inhibitor (PDI) and occur also in other Gammaproteobacteria, especially Vibrio. Their structure and biosynthesis were fully elucidated despite their instability, highlighting a rare trans-methylation of their N-terminus. Subsequently, the structure of the responsible methyltransferase XisE and the peptide deformylase XisD, serving as resistance mechanism, were elucidated by X-ray crystallography, allowing insights into the function and the mode of action of this novel class of PDIs.