Z-Form Stabilization By The Zα Domain Of Adar1p150 Has Subtle Effects On A-To-I Editing
Z-Form Stabilization By The Zα Domain Of Adar1p150 Has Subtle Effects On A-To-I Editing
Nichols, P. J.; Riemondy, K. A.; Krall, J. B.; Ramos, J.; Goering, R.; Henen, M. A.; Taliaferro, J. M.; Vogeli, B.; Vicens, Q.
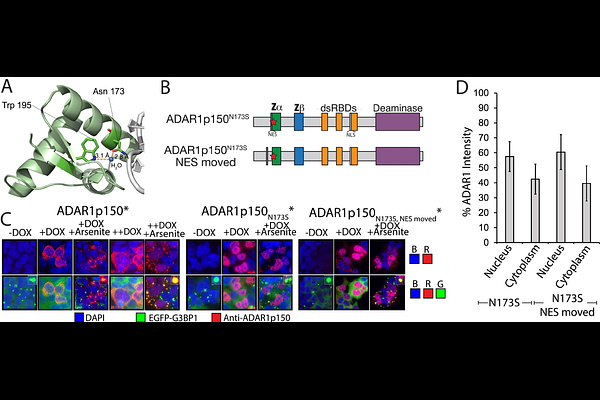
AbstractThe role of Adenosine Deaminase Acting on RNA 1 (ADAR1)\'s Z-conformation stabilizing Z domain in A-to-I editing is unclear. Previous studies on Z mutations faced limitations, including variable ADAR1p150 expression, differential editing analysis challenges, and unaccounted changes in ADAR1p150 localization. To address these issues, we developed a Cre-lox system in ADAR1p150 KO cells to generate stable cell lines expressing Z mutant ADAR1p150 constructs. Using total RNA sequencing analyzing editing clusters as a proxy for dsRNAs, we found that Z mutations slightly decreased overall A-to-I editing, consistent with recent findings. These decreases correlated with mislocalization of ADAR1p150 rather than reduced editing specificity, and practically no statistically significant differentially edited sites were identified between wild-type and Z mutant ADAR1p150 constructs. These results suggest that Zs impact on editing is minor and that phenotypes in Z mutant mouse models and human patients may arise from editing-independent inhibition of Z-DNA-Binding Protein 1 (ZBP1), rather than changes in RNA editing.