Disease progression modelling reveals heterogeneity in trajectories of Lewy-type alpha-synuclein pathology
Disease progression modelling reveals heterogeneity in trajectories of Lewy-type alpha-synuclein pathology
Mastenbroek, S. E.; Vogel, J. W.; Collij, L. E.; Serrano, G. E.; Tremblay, C.; Young, A. L.; Arce, R. A.; Shill, H. A.; Driver-Dunckley, E. D.; Mehta, S. H.; Belden, C. M.; Atri, A.; Choudhury, P.; Barkhof, F.; Adler, C. H.; Ossenkoppele, R.; Beach, T. G.; Hansson, O.
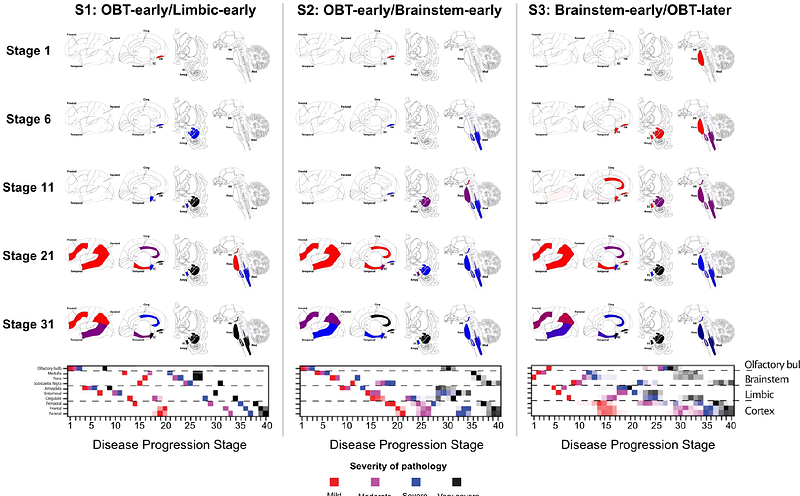
AbstractLewy body (LB) disorders, characterized by the aggregation of misfolded alpha-synuclein proteins, exhibit notable clinical heterogeneity. This may be due to variations in accumulation patterns of LB neuropathology. By applying data-driven disease progression modelling to regional neuropathological LB density scores from 814 brain donors, we describe three inferred trajectories of LB pathology that were characterized by differing clinicopathological presentation and longitudinal antemortem clinical progression. Most donors (81.9%) showed earliest pathology in the olfactory bulb, followed by accumulation in either limbic (60.8%) or brainstem (21.1%) regions. The remaining donors (18.1%) exhibited the first abnormalities in brainstem regions. Early limbic pathology was associated with Alzheimer\'s disease-associated characteristics. Meanwhile, brainstem-first pathology was associated with progressive motor impairment and substantial LB pathology outside of the brain. Our data provides evidence for heterogeneity in the temporal spread of LB pathology, possibly explaining some of the clinical disparities observed in LBDs.