Development of a cross-protective common cold coronavirus vaccine
Development of a cross-protective common cold coronavirus vaccine
Penaloza-MacMaster, P.; Dangi, T.; Li, S.
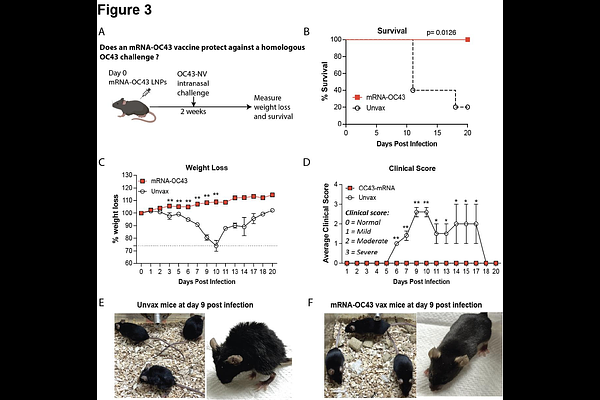
AbstractCommon cold coronaviruses, such as OC43 and HKU1, generally cause mild respiratory infections in healthy people. However, they can lead to severe illness in high-risk groups, including immunocompromised individuals and older adults. Currently, there is no clinically approved vaccine to prevent infection by common cold coronaviruses. Here, we developed an mRNA vaccine expressing a stabilized spike protein derived from OC43 and tested its efficacy in different challenge models in C57BL/6 mice. This novel OC43 vaccine elicited OC43-specific immune responses, as well as cross-reactive immune response against other embecoviruses, including HKU1 and mouse hepatitis virus (MHV-A59). Interestingly, this OC43 vaccine protected mice not only against a lethal OC43 infection, but also against MHV-A59, which is only 65% matched. Vaccine cross-protection appeared to be mechanistically mediated by non-neutralizing antibodies, but not by CD8 and CD4 T cells. These findings provide insights for the development of common cold coronavirus vaccines, demonstrating the potential for a single vaccine to target different members of a coronavirus subgenus.