Identification of Multi-landscape and Cell Interactions in the Tumor Microenvironment through High-Coverage Single-Cell Sequencing
Identification of Multi-landscape and Cell Interactions in the Tumor Microenvironment through High-Coverage Single-Cell Sequencing
Zhong, W.; Wang, L.; Guo, T.; zhao, l.; Wu, D.; Xie, F.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, F.; Gu, W.; Lin, T.; Chen, X.
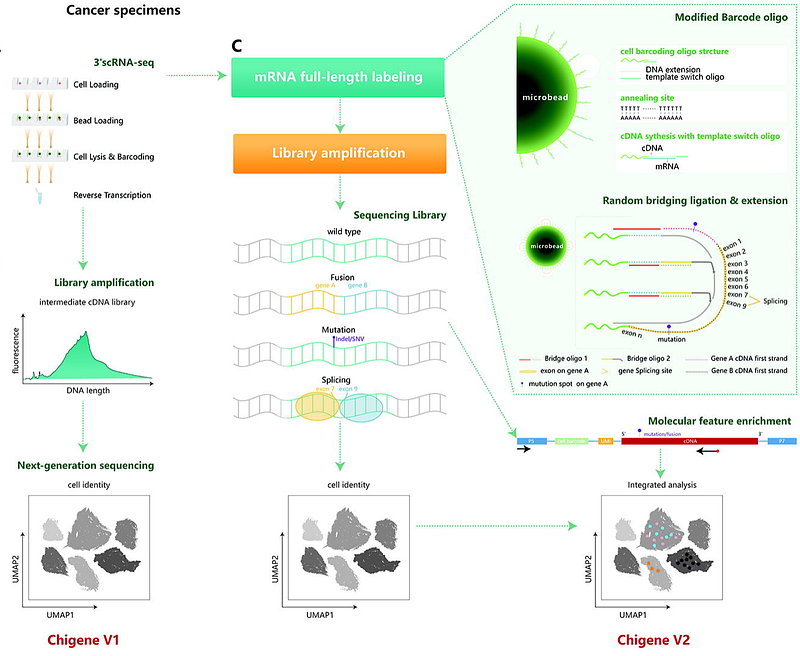
AbstractSingle-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) is a widely used method for classifying cell types and states and revealing disease mechanisms. However, most contemporary scRNA-seq platforms fail to explore the multi-landscape of RNA. Here, we designed a microfluidic chip combined oligo-dT primers and Random Bridging Co-labeling (RBCL) RNA sequencing to develop an innovative Chigene scRNA-seq technology that can identify gene expression, mutations, and RNA splicing landscapes at the single-cell level. The Chigene scRNA-seq platform demonstrated exceptional performance, with minimal doublet rates of 0.94% (Chigene V1) and 1.93% (Chigene V2). Both versions exhibit high sensitivity, with Chigene V2 achieving nearly 100% RNA coverage and detecting over 1800 genes per cell on average. Targeted capture of single-cell gene mutations enhances mutation detection sensitivity. Moreover, this Chigene V2 platform has been validated in clinical samples for its ability to detect mutations, gene fusions and alternative splicing. The reliability of the platform was further corroborated using known functional gene mutation (CDKN1A) and fusion (FGFR3-TACC). To validate this method\'s potential for discovering novel gene mutations in clinical samples, our investigation revealed an intriguing cell subpopulation carrying an ARHGAP5 mutation in urothelial carcinoma. These cells exhibited high-frequency mRNA splicing and exhibited specific crosstalk with T cells, distinguishing them from the subpopulation with the ARHGAP5 wild-type phenotype. Overall, this method provides a robust scRNA-seq platform suitable for comprehensive analyses of clinical specimens at different genetic information levels, thereby offering significant potential in the discovery of novel genes and interactions at the single-cell level.


