Efficiency and localisation of AURKA degradation by PROTACs is modulated by deubiquitinases UCHL5 and target-selective OTUD6A
Efficiency and localisation of AURKA degradation by PROTACs is modulated by deubiquitinases UCHL5 and target-selective OTUD6A
Cardno, A.; Roberts, K.; Lindon, C.
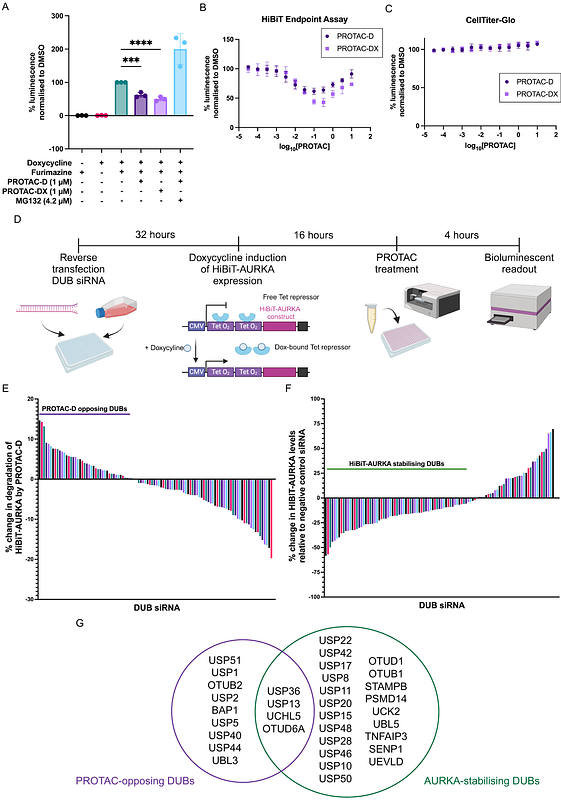
AbstractProteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs) represent a promising new drug modality for novel therapeutics. However, the cellular mechanisms and regulatory pathways underlying their activity are not fully understood. Here, we unveil the role of deubiquitinases (DUBs) in regulating PROTAC activity, by screening 97 human DUBs for their influence on degradation of cell-cycle kinase AURKA using siRNA-mediated knockdown. Our findings reveal that DUBs OTUD6A and UCHL5 counteract degradation of AURKA by small molecule PROTACs. Further investigation using orthogonal dTAG PROTACs indicates that the PROTAC-opposing effect of OTUD6A is target-specific for AURKA, while UCHL5 counteracts degradation triggered by other PROTACs dependent on ubiquitin ligase adaptor CRBN, but not VHL. Furthermore, we show that differential sensitivity of the nuclear pool of AURKA to PROTAC-mediated degradation is fully explained by the specific subcellular localisation pattern of OTUD6A. These findings enhance our understanding of cellular pathways underpinning the action of PROTACs and indicate that combinations of DUB inhibitors and PROTACs will lead to enhanced target degradation and potential improvement in therapeutic outcomes.