Translation Efficiency Impacts Phage Lysis Timing and Its Precision in Single Cells
Translation Efficiency Impacts Phage Lysis Timing and Its Precision in Single Cells
Kannoly, S.; Singh, K.; Juman, N.; Islam, Z. M.; Caballero Quiroga, I.; Singh, A.; Dennehy, J. J.
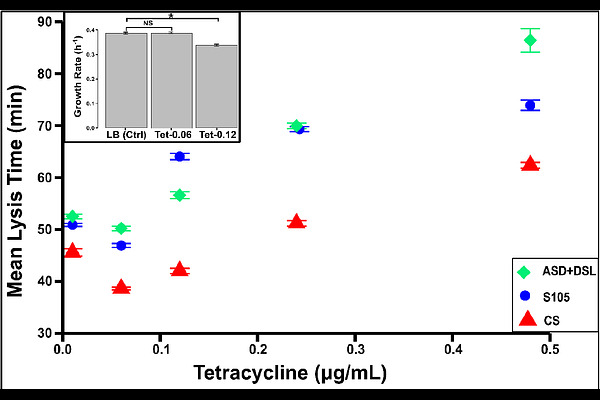
AbstractThe timing of host cell lysis is a fundamental life history parameter in bacteriophages as it presents an evolutionary trade-off between maximizing intracellular phage replication and optimizing transmission to new host cells, ultimately determining viral fitness in dynamic bacterial populations. In the bacteriophage {lambda}, lysis time is dependent on the expression of a timekeeper protein, holin, which accumulates in the Escherichia coli inner membrane. Cell lysis is triggered when the membrane concentration of holin crosses a critical threshold level. In the present study, we investigated the effects of the rate of holin translation on lysis timing and its precision. We show that modulating holin translation efficiency through genetic modifications and antibiotic treatment alters bacteriophage lysis timing and its precision, providing insight into how phages optimize the evolutionary trade-off between replication and transmission. Reducing ribosomal binding affinity decreased holin expression and delayed lysis, while optimizing the Shine-Dalgarno sequence enhanced translation and accelerated lysis. Surprisingly, very low tetracycline concentrations may have improved translation efficiency and hastened lysis, whereas higher doses predictably delayed it. In all cases, longer lysis times corresponded with decreased timing variability. A model that incorporates stochastic gene expression with additional stochasticity in the initiation of holin expression was sufficient to explain the data. Thus, we demonstrated that modifying the rate of holin translation can be used as an evolutionary strategy to achieve optimum lysis timing.