Neural population dynamics of human working memory
Neural population dynamics of human working memory
Li, H.-H.; Curtis, C. E.
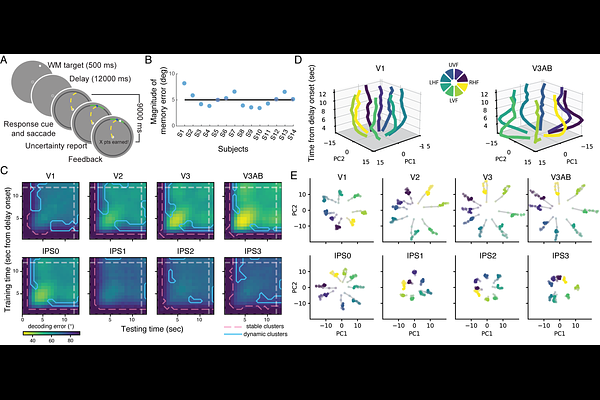
AbstractTemporally evolving neural processes maintain working memory (WM) representations of information no longer available in the environment. Nonetheless, the dynamics of WM remain largely unexplored in the human cortex. With fMRI, we found evidence of both stable and dynamic WM representations in human cortex during a memory-guided saccade task. The stability of WM varied across brain regions with early visual cortex exhibiting the strongest dynamics. Leveraging population receptive field modeling, we visualized and made the neural dynamics interpretable. Early in the trial, neural responses in V1 were dominated by narrowly tuned activation at the location of the peripheral target. Over time, activity spread toward foveal locations and targets were represented by diffuse activation among voxels with receptive fields along a line between the fovea and the target. We suggest that the WM dynamics in early visual cortex reflects a transformation of sensory inputs into abstract task-related representations.