Impaired envelope integrity in the absence of SanA is linked to increased Lipid II availability and an imbalance of FtsI and FtsW activities
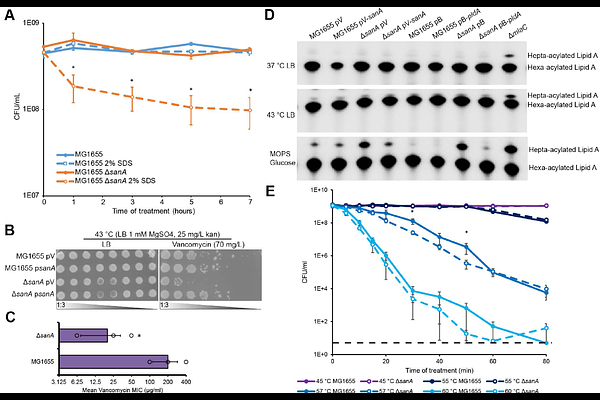
Impaired envelope integrity in the absence of SanA is linked to increased Lipid II availability and an imbalance of FtsI and FtsW activities
Carr, J. F.; De Santiago, C. B.; Bhut, S.; Warzecha, D. J.; Wei, R.; Herrera, C.; Trent, M. S.; Nan, B.; Mitchell, A.
AbstractIn gram-negative bacteria, the outer membrane (OM) acts in conjunction with the peptidoglycan (PG) cell wall as a barrier against physical, osmotic, and toxic environmental stresses including antibiotics. SanA, an inner membrane protein in Escherichia coli K-12, is required for vancomycin resistance at high temperatures (>42 {degrees}C) and we have previously demonstrated that SanA impacts sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) resistance during stationary phase reached from carbon limitation. However, its function remains unknown. Here, we show that {Delta}sanA has a synthetic genetic interaction with {Delta}wecA, a mutation increasing the availability of the isoprenoid carrier for PG biosynthesis. Specifically, the {Delta}sanA {Delta}wecA strain demonstrated heightened SDS EDTA sensitivity, Rcs stress response activation, and increased cell length. Further investigation tied the SDS EDTA sensitivity to increased Lipid II available for PG synthesis. Spontaneous suppressor mutants of this phenotype harbored point mutations in prc which encodes tail specific protease or ftsI which encodes the cell division DD-transpeptidase, a target of Prc. Given Prc\'s role in FtsI maturation, we focused on the ftsI mutations and determined these mutations caused a partial loss of function in FtsI, with at least one of these mutations also increasing FtsW activity. Moreover, we found that other mutations which reduce septal PG synthesis, but not divisome assembly, also suppressed the SDS EDTA sensitivity. Together, these findings demonstrates that, in the absence of SanA, increased Lipid II availability perturbs the balance between FtsI and FtsW function leading to increased OM permeability.