Potent Neutralization by Antibodies Targeting the Mpox A28 Protein
Potent Neutralization by Antibodies Targeting the Mpox A28 Protein
Yefet, R.; Battini, L.; Hubert, M.; Rakayev, K.; GUIVEL-BENHASSINE, F.; Rattner, N.; Porrot, F.; Abramovitz, L.; Ostashinsky, G.; Ben-Shalom, N.; Postal, J.; Polonsky, K.; Ralph-Altman, M.; Sweed, S.; Korner, T.; Friedel, N.; Hagin, D.; Sprecher, E.; Fishelson, Z.; Kobiler, O.; Adler-Abramovich, L.; Schwartz, O.; Guardado-Calvo, P.; Freund, N.
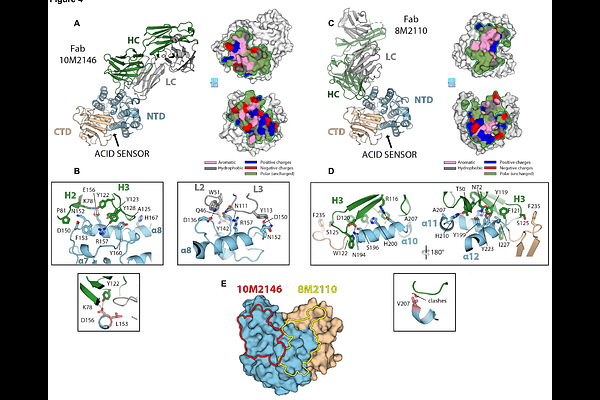
AbstractMpox is the most pathogenic Poxvirus in circulation. While several antigens have been identified as targets for neutralizing antibodies, many proteins remain unexplored. We isolated and characterized four monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) targeting the Mpox A28 (OPG153), a virulence factor present on mature Mpox virions. The antibodies were isolated from convalescent individuals, alongside 14 additional mAbs targeting the A35 and H3 proteins. Anti-A28 mAbs potently neutralized Mpox and Vaccinia virus (VACV) through complement-dependent mechanisms involving C1q and C3 deposition. High resolution crystal structures of Anti-A28 mAbs 10M2146 and 8M2110 in complex with VACV A26 revealed two proximal epitopes within the N-terminal domain. Passive transfer of 8M2110 attenuated disease in infected mice. Moreover, immunization with A28 elicited antigen-specific B cells and robust neutralizing antibody responses and provided complete protection against lethal VACV challenge. These findings support Mpox A28 as a promising target for the induction of neutralizing antibodies and antiviral interventions.