Numerical experiments for reconstructing cerebrospinal fluid flow based on contrast enhanced magnetic resonance images in the lower subarachnoid compartments of the brain
Numerical experiments for reconstructing cerebrospinal fluid flow based on contrast enhanced magnetic resonance images in the lower subarachnoid compartments of the brain
Hornkjol, M.; Valnes, L. M.; Mardal, K.-A.
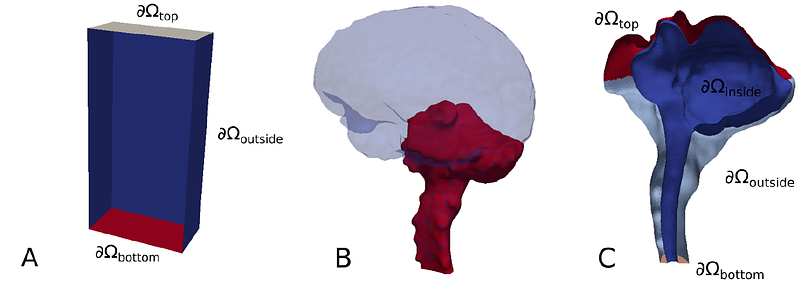
AbstractIn this paper we test various numerical methods for flow reconstruction based on both manufactured, idealized data and real patient data based on contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging after intrathecal contrast injection. As shown in previous studies, the imaging often display contrast gradients in localized regions although large areas have very small gradients. Velocities may as such be hard to assess in areas of low gradients. We compare optimal mass transfer with adjoint based data assimilation constrained by a convection diffusion equation. With well-chosen parameters the manufactured problems can be solved well in the idealized setting, but the performance is in general significantly worse in the patient specific setting. The methods predict maximal velocities well, but fail to reconstruct accurate velocity fields in areas without contrast gradients.