Phactr4 influences macrophage lamellipodial structure and dynamics through Arp2/3 complex and Ezrin regulation
Phactr4 influences macrophage lamellipodial structure and dynamics through Arp2/3 complex and Ezrin regulation
Manickam, R.; Rotty, J. D.
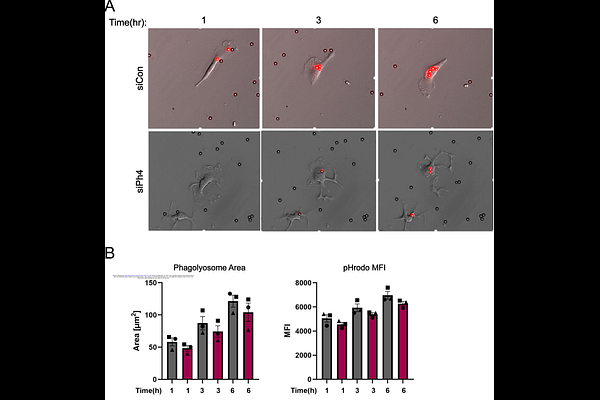
AbstractDynamic cycles of actin remodeling drive membrane protrusion and retraction events essential for macrophage function. Phosphoregulation of actin-associated proteins plays a key role, but the factors that determine the spatiotemporal balance between kinases and phosphatases is less well understood in this context. Here, we identify the Protein Phosphatase 1 (PP1)-binding protein Phactr4 as a critical regulator of cytoskeletal remodeling. Phactr4 loss disrupts lamellipodial architecture, which results in uncoordinated migration and disrupted iC3b-mediated phagocytosis. Unstable membrane dynamics underlie the Phactr4 knockdown phenotypes. Phactr4 is recruited to the leading edge via interaction with active Arp2/3 complex, and strongly correlates with membrane retraction. Phactr4 loss leads to ezrin hyperphosphorylation, and membrane protrusion defects in these cells are reversed by ezrin inhibition. Our findings position Phactr4 as a critical PP1-dependent coordinator of cytoskeletal remodeling during macrophage migration and phagocytosis. Recent reports have linked Phactr4 to several human disease states, which may be due to its influence on actin dynamics.