Analysis of coding gene expression from small RNA sequencing
Analysis of coding gene expression from small RNA sequencing
Azadova, A.; Ekperuoh, A.; Brooke, G. N.; Marco, A.
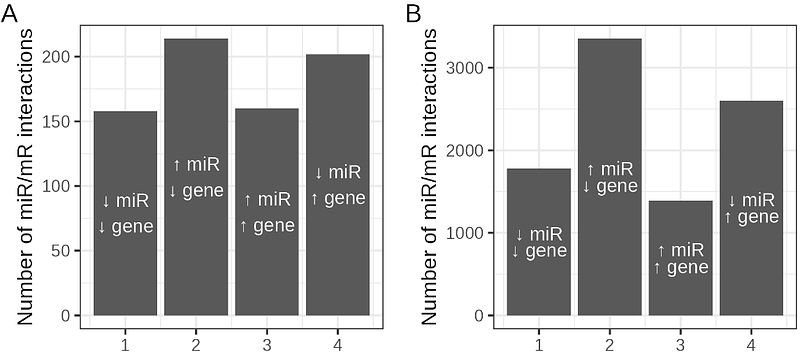
AbstractThe popularity of microRNA expression analyses is reflected by the existence of thousands of works in the literature in which sRNAseq has been performed in myriads of samples, but for which no matched total RNAseq exists. The lack of paired sequencing experiments severely restricts the analysis of microRNA-gene regulatory networks. We therefore explored whether protein-coding gene expression can be quantified from transcript fragments present in sRNAseq experiments. We first considered studies containing matched total RNA and small RNA from four human tissues and recovered transcript fragments from the small RNA experiments. We found that the expression levels of protein-coding gene transcripts from sRNAseq datasets was comparable to those from total RNAseq experiments (R2 ranging 0.33-0.76). We then analysed the expression of both microRNAs and coding genes from the same sRNAseq experiments and demonstrated that known microRNA-target interactions are, as expected, inversely correlated with the expression profiles of these microRNA-mRNA pairs. To confirm the utility of this approach, we applied our method to investigate microRNAs and their targets in breast cancer patient samples for which only sRNAseq was performed and only microRNAs studied. We again identified a clear inverse correlation between the expression of microRNAs and mRNAs that they are predicted to regulate (i.e. presence of a target site). We also found that upregulation of mir-429 is associated with the downregulation of QKI, an RNA-binding protein, in breast cancer samples. In conclusion, although the analysis of mRNA fragments to study gene expression from sRNAseq experiments may have its limitations, it can be very informative in the study of microRNA-mRNA interactions.


