RNA virus-mediated gene editing for tomato trait breeding
RNA virus-mediated gene editing for tomato trait breeding
Uranga, M.; Aragones, V.; Garcia, A.; Mirabel, S.; Gianoglio, S.; Presa, S.; Granell, A.; Pasin, F.; Daros, J.-A.
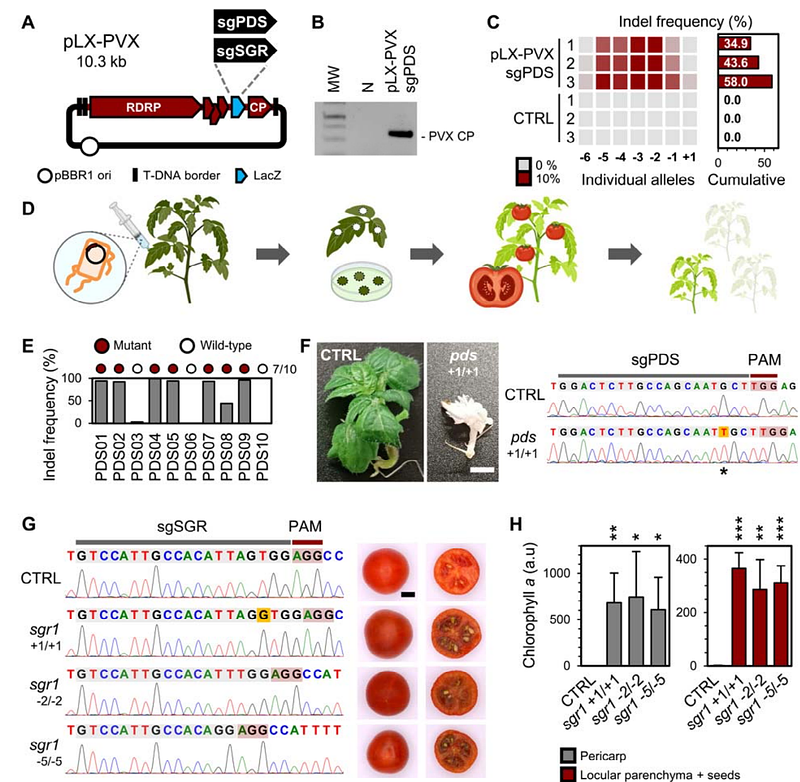
AbstractVirus-induced genome editing (VIGE) is a flexible and robust technology that relies on viral vectors for the transient delivery of CRISPR-Cas components into plants. Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) is a mayor horticultural crop grown worldwide; despite its economic importance, little is known about VIGE applicability in this species. This study presents the successful use of VIGE in tomato for fruit color breeding. We report (i) the generation of a transgenic Cas9-expressing line of tomato cv. Micro-Tom (MT-Cas9), (ii) the use of pLX-PVX, an enhanced RNA viral vector, for single-guide RNA (sgRNA) delivery into MT-Cas9 plants, (iii) heritable, proof-of-concept VIGE of PHYTOENE DESATURASE and recovery of albino progeny, and (iv) the recovery of progeny with recolored green-flesh fruits by VIGE of STAYGREEN 1, thus confirming the successful breeding of tomato fruit color. Altogether, our results indicate that the presented VIGE approach can be readily applied for accelerated functional genomics of tomato variation, as well as for precision breeding of tomato traits with horticultural interest.