Evidence for GeV Gamma-Ray Emission from Intense GRB 240529A During the Afterglow's Shallow Decay Phase
Evidence for GeV Gamma-Ray Emission from Intense GRB 240529A During the Afterglow's Shallow Decay Phase
Kenta Terauchi, Tomohiko Oka, Katsuaki Asano
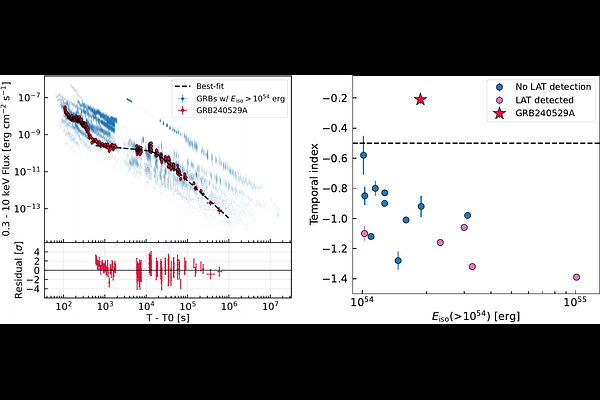
AbstractX-ray light curves of gamma-ray burst (GRB) afterglows exhibit various features, with the shallow decay phase being particularly puzzling. While some studies report absence of the X-ray shallow decay for hyper-energetic GRBs, recently discovered GRB 240529A shows a clear shallow decay phase with an isotropic gamma-ray energy of \SI{2.2e54}{erg}, making it a highly unusual case compared to typical GRBs. In order to investigate the physical mechanism of the shallow decay, we perform the \textit{Fermi}-LAT analysis of GRB 240529A along with \textit{Swift}-XRT analysis. We find no jet break feature in the X-ray light curve and then give the lower bound of the collimation-corrected jet energy of $>10^{52}$~erg, which is close to the maximum rotational energy of a magnetar. Our LAT data analysis reveals evidence of GeV emission with a statistical significance of $4.5\sigma$ during the shallow decay phase, which can be interpreted as the first case for hyper-energetic GRBs with a typical shallow decay phase. The GeV to keV flux ratio is calculated to be $4.2\pm2.3$. Together with X-ray spectral index, this indicates an inverse Compton origin of the GeV emission. Multiwavelength modeling based on time-dependent simulations tested two promising models, the energy injection and wind models. Both models can explain the X-ray and gamma-ray data, while our modeling demonstrates that gamma-ray observations, along with future GeV--TeV observations by CTAO, will distinguish between them.