Modeling the circumstellar interaction around SN 2004gq
Modeling the circumstellar interaction around SN 2004gq
A. P. Nagy, B. H. Pál, T. Szalai
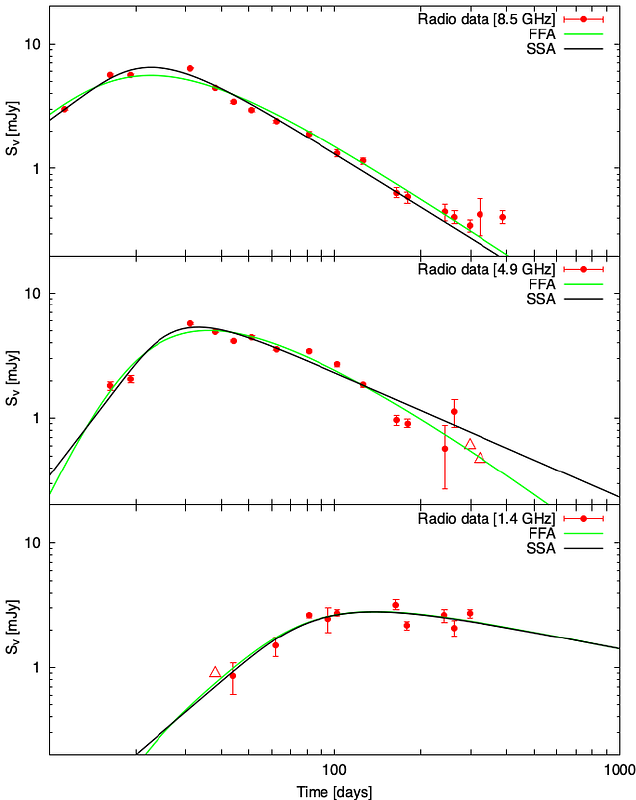
AbstractThe relationship between the mass-loss history and final evolutionary stage of massive stars and the properties of the observable supernova (SN) is still under debate. This is especially true for stripped-envelope (Type Ib/c) SNe, where the progenitor ejects a considerably large amount of material during its evolution, which can lead to a circumstellar medium relatively close to the exploding star. Moreover, when the star explodes as a SN, this matter may contribute significantly to the generated luminosity because of the interaction. However, the trace of this circumstellar interaction can only be investigated for a couple of Type Ib/c SNe, and the nature of a close (within around $10^{15}$ cm) circumstellar matter (CSM) has also been largely unexplored for these objects. Here, we present the results of our radio and bolometric light curve (LC) analysis related to SN 2004gq. We describe a combined model that explains the unusual LC properties of this event and supports the circumstellar interaction scenario. For that, we computed the quasi-bolometric LC of the SN and fit this with a multicomponent model to gain information on the progenitor and the surrounding circumstellar medium. We also analyzed the available radio LCs (taken at 1.4,\ 4.9 and 8.5 GHz) of SN 2004gq to verify our estimated average mass-loss rate, which is one of the most crucial physical properties related to CSM models. We infer reasonable parameters for SN 2004gq using radioactive decay and magnetar energy input. To power the entire LC, we must also add an extra energy source related to the CSM. We determine the most essential parameter of this medium: the average mass-loss rate from both LC and radio data fitting. We find that the suggested hidden circumstellar interaction is a viable mechanism that provides the required energy deficiency and that it can be estimated using a simple semi-analytic model.