SNR G54.1+0.3, a PeVatron candidate unveiled by LHAASO
SNR G54.1+0.3, a PeVatron candidate unveiled by LHAASO
Yihan Shi, Yudong Cui, Lili Yang
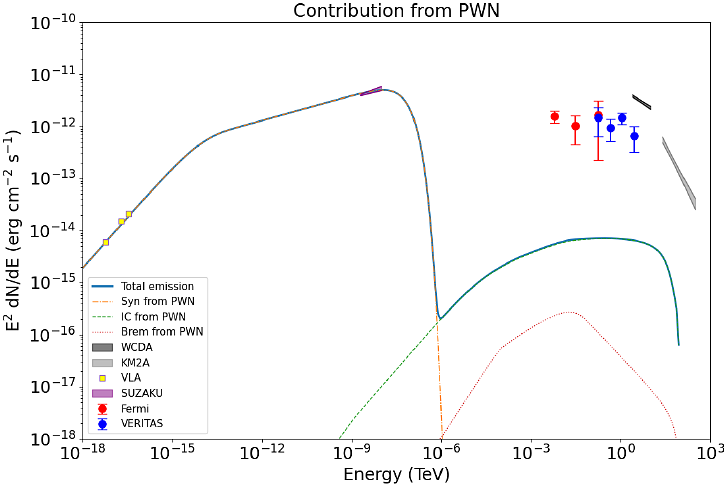
AbstractRecently, the LHAASO Collaboration reported the first very-high-energy gamma-ray catalog, containing 90 TeV sources. Among these sources, 1LHAASO J1929+1846u is located 0.3$^\circ$ west of SNR G54.1+0.3 and also lies within a $+53 \, \text{km s}^{-1}$ cloud (the Western Cloud). Moreover, one of the IceCube track-type high-energy starting events is found around 1.3$^\circ$ north of 1LHAASO J1929+1846u, which may serve as strong evidence for the hadronic origin of this TeV source. SNR G54.1+0.3 is a young supernova remnant (SNR), with a powerful pulsar wind nebula (PWN) inside. Its X-ray radiation from the PWN and the SNR Shell can be clearly identified. The radio emission from the PWN region is also given. However, given the angular resolution of gamma-ray experiments, the entire SNR region is viewed as a point source by Fermi-LAT, H.E.S.S. and VERITAS. In this work, we explore a hybrid scenario where SNR G54.1+0.3 is indeed associated with the Western Cloud, and we derive the multi-wavelength emissions from the PWN, the SNR Shell, and the Western Cloud, separately. Our model can explain the observations well, indicating that SNR G54.1+0.3 might be an excellent candidate of Galactic PeVatron and neutrino source.