Resonant amplification of multi-messenger emission in rotating stellar core collapse
Resonant amplification of multi-messenger emission in rotating stellar core collapse
Marco Cusinato, Martin Obergaulinger, Miguel-Ángel Aloy, José-Antonio Font
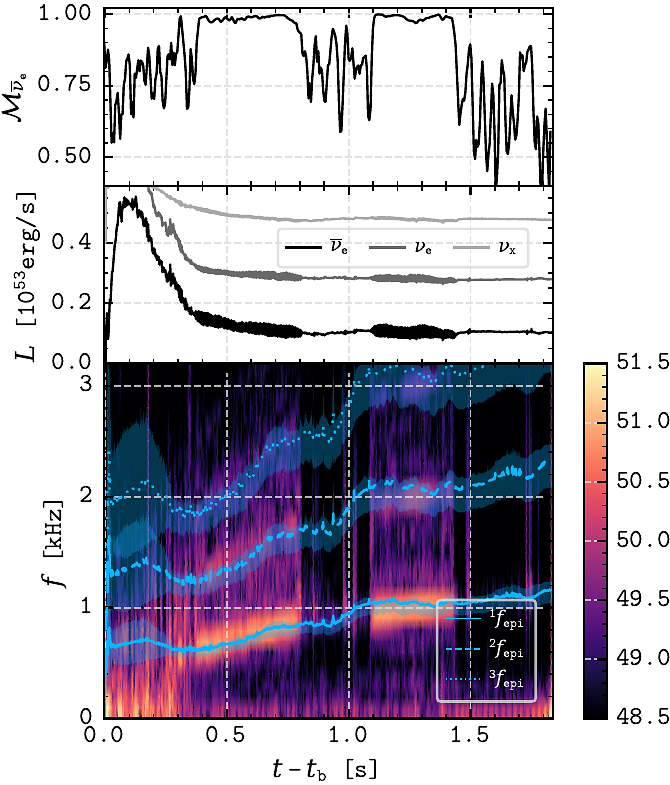
AbstractIn a series of axisymmetric core-collapse supernova simulations extending up to $\sim 2\,\mathrm{s}$, we identify a regime of pre-collapse central rotation rates ($\sim 1\,\mathrm{Hz}$) that greatly enhances the emission of gravitational waves (GWs) during extended periods of time after bounce. The enhancement is a consequence of the resonance between the frequency of the fundamental quadrupolar $^2f$-mode of oscillation of the proto-neutron star and the frequency of the epicyclic oscillations at the boundary of the inner core. We observe periods of about several hundred milliseconds each where the resonance is active. The GW emission enhancement produces a correlated resonant modulation of the associated neutrino signal at the same frequencies. With GW frequencies of $\mathcal{O}(1\,\mathrm{kHz})$ and strain amplitudes within the sensitivity curves of current and next-generation interferometers at distances of $\mathcal{O}(1\,\mathrm{Mpc})$, this resonant-amplification mechanism may represent a potential game-changer for unveiling the supernova explosion mechanism through multi-messenger astronomy.