A new independent look at the galactic black hole low-mass X-ray binary distribution
A new independent look at the galactic black hole low-mass X-ray binary distribution
Youssef Abdulghani, Anne M Lohfink, Jaiverdhan Chauhan
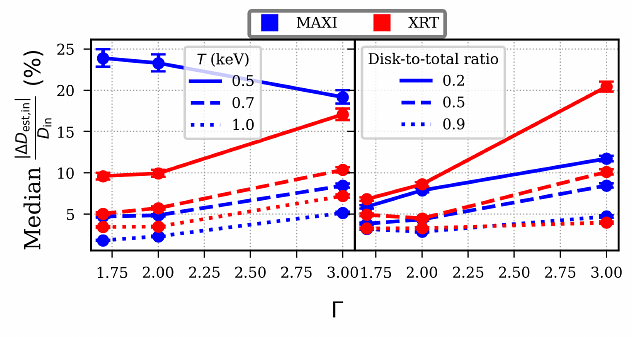
AbstractInvestigations of the Galactic black hole low-mass X-ray binaries (BH-LMXBs) offer valuable insights into the elusive black hole population in the Milky Way. Motivated by recent tensions in the natal kick velocity distribution and BH mass distribution of BH-LMXBs, we revisit the spatial distribution of the Galactic BH-LMXBs using a new set of distance measurements obtained from an X-ray spectral modelling framework that we introduced in earlier work. We perform a multiparameter simulation study to mitigate part of the bias present in our prior estimates and gain insights into possible observational selection effects that affect the observed population. We derive a bias correction factor, well described by a Pareto probability density function that closely follows an inverse-square law dependence on distance. We then construct a bias-corrected, literature-independent, Galactic spatial distribution that clearly traces spiral arm structures and shows a deficit of sources very close to the Galactic centre, which might be explained due to high extinction or a true paucity of these sources at that region. Further analysis of the simulation results provides hints for a hidden population of BH-LMXBs at low Galactic heights. Lastly, we estimate the root-mean-squared Galactic height and find that it is most compatible with a hybrid scenario of BH formation, with some BHs receiving high natal kicks and thus propelled further from the thin disc plane while others receiving low natal kicks and remaining close to their birth place.